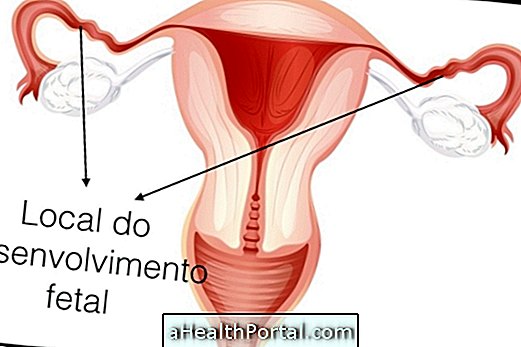
Ectopic pregnancy, or tubal pregnancy, is a gestation that occurs outside the uterus inside the fallopian tubes, which is doomed to not develop because it is not possible to move the embryo into the uterus, and the fallopian tubes are unable to distend, as the uterus succeeds, and so breaks, endangering the woman's life.
The main causes of ectopic pregnancy, which is when the embryo is developing outside the uterus, are to use the IUD, have endometriosis, chlamydia or have already had a tubal ligation.
Normally, ectopic pregnancy is identified up to 10 weeks' gestation on an ultrasound but it can also be discovered later. However, if the problem is not detected, the tube may rupture, being called a ruptured ectopic pregnancy, which can cause internal bleeding, which can be fatal.
Signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy
Some signs and symptoms that may indicate pregnancy outside the uterus include the pain of only one side of the belly, which gets worse every day, always localized, and vaginal bleeding, which can start with a few drops of blood, but in a short time it becomes stronger.
The pharmacy pregnancy test can detect that the woman is pregnant, but it is not possible to know if it is ectopic pregnancy, and it is necessary to perform an ultrasound examination to verify exactly where the baby is located. As the ectopic pregnancy becomes a route before the 12th week of gestation, there is no time for the belly to begin to grow sufficiently to be noticed by other people. Learn more details of symptoms and diagnosis of tubal pregnancy.
In a normal gestation, with Beta HCG between 1000 and 2000 mIU / ml, the gestational sac must be seen inside the uterus by transvaginal ultrasonography.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Possible causes of ectopic pregnancy include:
- Use IUD;
- Scar of pelvic surgery;
- Pelvic inflammation;
- Endometriosis, which is the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus;
- Previous ectopic pregnancy;
- Salpingitis: Inflammation or deformation of the Fallopian tubes;
- Complications of Chlamydia;
- Fallopian tube surgery;
- Malformation of fallopian tubes;
- In case of infertility;
- Have tubal ligation done.
There are also factors that increase a woman's risk of having an ectopic pregnancy, such as age above 35, in vitro fertilization, and having multiple sex partners. See more on how inflammation in the tubes can make pregnancy difficult.
Treatments for ectopic pregnancy
Treatment for ectopic pregnancy, which develops in the tube or ovary, can be done through the use of the drug methotrexate, which induces abortion or surgery to remove the embryo and rebuild the tube.
When the remedies are indicated
The doctor may decide to use drugs such as methotrexate 50 mg in the form of an injection when ectopic pregnancy is discovered before 8 weeks of gestation, the woman has no rupture of the tube, the gestational sac is less than 5 cm, the Beta HCG is less than 2, 000 mIU / ml and the heart of the embryo is not beating.
In this case the woman takes 1 dose of this medicine and after 7 days must realize a new Beta HCG until it is undetectable. If your doctor thinks you are safer, you may want to give another 1 dose of this drug to make sure the problem is fixed. The Beta HCG should be repeated in 24 hours and then every 48 hours to check if it is gradually lowering.
During this treatment that can last up to 3 weeks is recommended:
- Do not take the vaginal touch exam because it can cause tissue tearing;
- Do not have intimate contact;
- Avoid sun exposure as the remedy can stain the skin;
- Do not take anti-inflammatories because of the risk of anemia and gastrointestinal problems related to the remedy.
Ultrasound can be performed once a week to check if the mass disappeared because even though the values of beta HCG are decreasing, there is still the possibility of rupture of the tube.
When surgery is indicated
Surgery to remove the embryo can be done by laparostomy or open surgery and is indicated when the embryo is more than 4 cm in diameter, the Beta HCG test is more than 5000 mIU / ml or when there is evidence of rupture of the embryo. which puts the woman's life at risk.
In either case, the baby can not survive and the embryo must be completely removed and can not be implanted into the uterus.
Is it possible to become pregnant after the surgery?
If the tubes have not been damaged by ectopic pregnancy, the woman has a new chance of re-conceiving, but if one of the tubes has ruptured or become injured, the chances of becoming pregnant again are much lower, and if the two tubes ruptured or are affected, the The most feasible solution will be in vitro fertilization.
Find out how much time it takes to get pregnant and tips to speed this process on: How to Get Pregnant After a Tubal Pregnancy
Types of ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a rare condition, the most common being that it develops in one of the tubes, but it can also develop in other parts of the body, so there may be ectopic pregnancy in the ovary, abdominal ectopic pregnancy or a cervical ectopic pregnancy, which is when the fetus grows in the cervix. The less common types of ectopic pregnancy are:
- Ectopic interstitial pregnancy: Occurs when the embryo develops in the interstitial segment of the tuba. In this case there is an increase of Beta HCG and the treatment is usually done with medicines and potassium chloride, in several doses;
- Cervical pregnancy: This is when the embryo develops in the cervix, which can lead to intense bleeding. Treatment may be done with embolization, curettage or local injection of methotrexate, for example;
- Ectopic pregnancy in the cesarean scar: It is very rare, but it can happen, requiring treatment with methotrexate and folinic acid for about 1 week;
- Ovarian Pregnancy: Sometimes it is only discovered during curettage and therefore methotrexate is not used;
- Heterotopic pregnancy: It is when the embryo develops between the uterus and the fallopian tube, but is usually only diagnosed after the rupture of the tube, so the most commonly used treatment is surgery.
Besides these types, there is also abdominal ectopic pregnancy, which is when the baby develops in the peritoneum, between the organs. This is a very rare condition and each case should be evaluated individually. This is a complicated pregnancy because as the baby grows, the mother's organs are being compressed and the blood vessels can be ruptured, being potentially fatal. However, there are reports of women who managed to get the baby to 38 weeks of gestation, and a cesarean section was performed at birth.