Changes in urine and difficulty maintaining erection are signs that may indicate prostate cancer, a common illness after age 50. However these same symptoms can also occur due to benign changes, such as in the enlarged prostate, for example. Therefore, it is important to go to the urologist at least once a year after the age of 45 to do routine exams to identify any prostate changes as soon as possible.
The prostate is a gland that is located near the anus and so rectal examination is the best way to evaluate your health. It is the prostate that produces the fluid that forms the sperm which is important for conducting the sperm to the ovum during sexual contact.
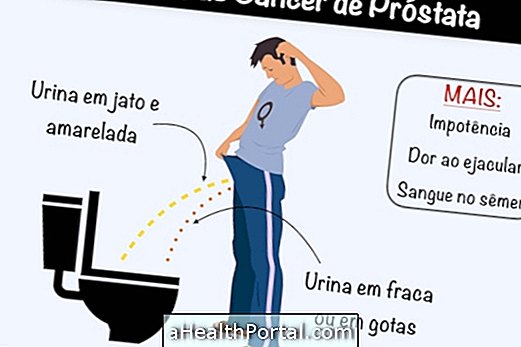
Early symptoms of prostate cancer
One must be aware of the following signs, which may indicate a tumor in the prostate:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Decrease in the amount of urine;
- Difficulty in stopping the passage of urine;
- Frequent urge to urinate, waking up several times during the night to go to the bathroom;
- Feeling that the bladder is still full, even after urinating;
- Urinate in drops;
- Pain in the region of the testicles;
- Impotence or difficulty in maintaining erection;
- Pain when ejaculating;
- Presence of blood in the semen.
In addition, if the cancer has spread to other regions of the body, it is also common to have symptoms such as back, thigh, shoulder or other bone pain, for example.
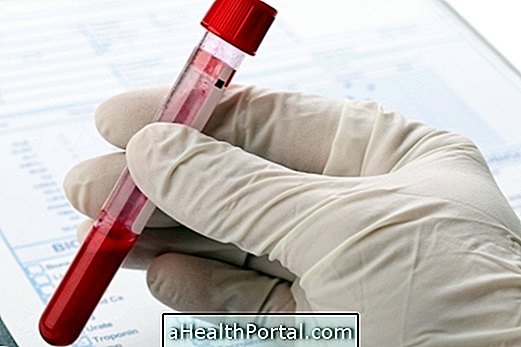
If any of these symptoms develop, you should see your urologist for tests that identify changes in the prostate, such as the rectal examination and PSA, which is a blood test. See which tests are done to evaluate the prostate and male health.
Symptoms of advanced prostate cancer
In more advanced cases, where the prostate is greatly enlarged or cancer metastasis has occurred to other regions of the body, the symptoms may include:
- Urinary or faecal incontinence;
- Weakness in the legs;
- Pain in the bones;
- Renal insufficiency.
In the more advanced stages, it is important to seek the doctor to assess the extent of the disease and whether other organs have been reached with the aid of exams such as prostate biopsy, scintigraphy or computed tomography.
Watch the following video and see what symptoms indicate prostate problems and what tests can be done:

Treatment for prostate cancer
Treatment for prostate cancer is done according to the stage of the disease and the state of health of the patient. Usually the treatment is done with:
- Surgery: it is the most used treatment, because it removes the prostate and in the initial cases of the disease, it brings the total cure;
- Radiotherapy: used in cases where surgery is contraindicated or when the patient does not want to be operated;
- Hormones: are used to control the production of hormones that promote the development of the disease.
In more advanced cases of the disease usually two of these treatment methods are used, being often necessary to withdraw beyond the prostate, the testicles as well.
The prostate enlargement is not always indicative of cancer, although it causes the same symptoms. See what the major prostate changes are and how to treat each one.