Kidney transplantation aims to restore kidney function by replacing a diseased kidney with a healthy kidney from a healthy and compatible donor.
Kidney transplantation is usually used as a treatment for chronic kidney failure or in patients who have multiple hemodialysis sessions per week. The transplant usually lasts between 4 and 6 hours and is not very suitable for people who have injuries to other organs such as cirrhosis, cancer or heart problems, as it can increase the risks of the surgical procedure.
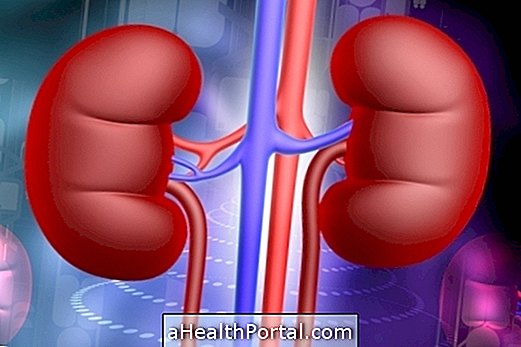
How is the transplant done?
Kidney transplantation is indicated by the nephrologist in cases of multiple hemodialysis per week or, more often, advanced chronic kidney disease after renal function analysis by laboratory tests. The transplanted kidney may be from a living donor, without any disease, and may or may not be related to the patient, or from an already deceased donor, in which case the donation can only be made after confirmation of brain death and family authorization.
The kidney of the donor is taken along with a portion of the artery, vein and ureter, through a small incision in the abdomen. In this way, the transplanted kidney is placed in the recipient, the portions of the vein and artery are attached to the veins and arteries of the recipient and the transplanted ureter is connected to the bladder the patient. The nonfunctional kidney of the transplanted person is not usually taken away because its poor function is useful when the transplanting kidney is not yet fully functional. The diseased kidney is only removed if it is causing infection, for example.
Kidney transplantation is performed according to the patient's health condition and is not very indicated in people who have heart, liver or infectious diseases, for example, because it may increase the risks of the surgical procedure.
Kidney Transplant Compatibility
Before transplantation is performed, blood tests should be performed to check the compatibility of the kidneys to reduce the chances of organ rejection. In this way, donors may or may not be related to the patient who will be transplanted, provided there is compatibility.
How is the postoperative
Recovery after kidney transplantation is simple and lasts for about three months. The patient should be hospitalized for a week so that signs of reaction to the surgical procedure can be closely observed and treatment can be done immediately. In addition, during the three months is indicated not to perform physical activities and conduct weekly examinations during the first month, spacing for two monthly consultations until the 3rd month due to the risk of rejection of the organ by the body.
Usually the use of antibiotics to prevent possible infections and immunosuppressive drugs is indicated after surgery to avoid rejection of the organ. These medicines should be used according to medical advice.
Possible risks and complications
Some complications of kidney transplantation may be:
- Rejection of the transplanted organ;
- Generalized infections;
- Thrombosis or lymphocele;
- Fistula or urinary obstruction.
To avoid serious complications, the patient should be alert to warning signs that include fever greater than 38 ° C, burning on urination, weight gain in a short time, frequent coughing, diarrhea, difficulty in breathing or swelling, heat and redness at the wound. It is also essential to avoid contact with sick people and polluted places and to make a correct and adapted diet. Learn how feeding is done after kidney transplantation.