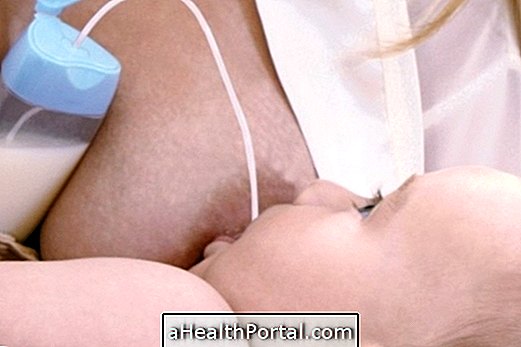
The first choice in feeding the baby in the first months of life should always be breast milk, but this is not always possible, and it may be necessary to use infant formula as alternatives to breast milk, which have a very similar nutritional composition, adequate for each stage of the baby's growth.
In addition to these formulas, children's milk is also available for specific medical purposes, which allow adequate nutrition even in cases of allergies, regurgitation, food intolerance, gastrointestinal disorders, among others.

When to give milk adapted for the baby
Breastmilk should be the first choice to feed the baby as it provides all the nutrients needed for its growth and development, as well as antibodies to enrich the immune system. See more about breast milk composition.
However, there are situations in which the mother can not or should not breastfeed, or in which the baby has some condition and can not digest the breast milk.
1. The mother is doing treatments
In cases where the mother is doing treatments that can harm the baby, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy, treatment for tuberculosis or treatments with medicines that pass into the milk, an adapted milk must be given, since the quality of the milk is compromised.
If the mother is a drug user, she should also not breastfeed, as these also pass into the milk and then ingested by the baby.
2. The mother has no milk or decreased production
Adapted milk can also be used when there is a decrease in milk production, which may or may not be temporary. There are also cases where the rise of milk happens later, and there may be changes in its composition.
It is therefore very important to go to the doctor regularly in order to improve this problem or to adapt the milk according to the condition of the mother and the baby.
3. The mother has an illness
If the mother has HIV, breast cancer or disturbances of consciousness, she should not give her milk to the baby. In addition, if you have diseases caused by viruses, fungi, bacteria, hepatitis B or C with high viral load, or active herpes in the breast or nipple, you should stop breastfeeding temporarily until the problem is resolved.
In temporary cases you will have to choose infant milk and keep the milk production, making it withdraw with a pump until you can breastfeed again after being cured. In cases where there is no other solution, one should choose infant formula and talk to the doctor to dry the milk. Learn how to dry your breast milk.

4. The baby is underweight
In cases where the baby is underweight for his or her age, reinforcement with an adapted milk may be recommended. However, breast milk can still be given to the baby.
5. The baby can not digest the milk correctly
If your baby has phenylketonuria or galactosemia, you should not breast feed or use regular infant formula.
In the case of phenylketonuria, non-phenylalanine-adapted milks may be used and, if the physician advises, take very cautious breast milk by weekly measurement of phenylalanine levels in the blood. Learn how to breastfeed a baby with phenylketonuria.
If the baby has galactosemia, he should not be breastfed or take infant formulas containing milk, and should be fed with soy-based formulas such as Nan Soy or Aptamil Soy. See more about what the baby with galactosemia should eat.

What milk to give to the baby
In cases where the baby can not take breast milk, cow's milk should never be given because it can impair its development, since its composition is very different from breast milk.
Then, with the help of the pediatrician, one should choose a suitable milk for the baby, which although not equal to the breast milk, has a more close composition, being enriched to offer the nutrients that the baby needs in each phase.
1. Regular children's milk
Regularly adjusted milks can be used by healthy infants without risk of allergies, gastrointestinal discomfort or metabolic diseases.
There are several brands available for sale, all having a similar nutrient composition, and may or may not be supplemented with probiotics, prebiotics, long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and nucleotides.
The choice of infant formula should take into account the age of the baby, because throughout its development it will have specific needs. Then between 0 and 6 months should be used a starting milk, such as Aptamil profutura 1, Milupa 1 or Nan supreme 1, and from 6 months should be given a transition milk as Aptamil 2 or Nan supreme 2, for example.
2. Milk for babies with cow's milk protein allergy
Allergy to cow's milk protein is the most frequent food allergy in childhood, in which the immune system is still immature and sensitive to antigens, and therefore reacts in the presence of cow's milk protein causing symptoms such as generalized redness and itching, vomiting and diarrhea. Learn more about baby milk allergy.
There is a wide variety of milks for this specific problem, which usually have the cow's milk protein divided into small fragments, or even divided into amino acids, so as not to provoke allergies, or can also be derived from soy:
- Extensively hydrolyzed, lactose-free formulas such as: Pregomin pepti, Alfaré, Nutramigen Premium ;
- Widely hydrolyzed formulas, with lactose as: Aptamil pepti, Althéra ;
- Formulas based on amino acids like: Neocate LCP, Neo advance, Neoforte ;
- Soy formulas like: Aptamil Proexpert soy, Nan soy .
About 2 to 3% of children are allergic to cow's milk protein in childhood, developing mostly tolerance to cow's milk between 3 and 5 years of age. In cases of infants who need to take synthetic milk and have a family history of allergies, they should take a hypoallergenic milk, known as HA milk.

3. Refillable baby milk
Gastroesophageal reflux is common in healthy infants due to the immaturity of the esophageal sphincter and involves the passage of food from the stomach into the esophagus, resulting in frequent gnawing. In such cases, it can lead to weight loss and malnutrition being detrimental in the baby's development. See more about reflux in babies.
Thus, there are antireflux milks such as Aptamil AR, Nan AR or Enfamil AR Premium, wherein the composition is the same as the other formulas, but are thicker due to the addition of corn starch, potato or rice, carob or jatai gum.
The presence of these thickeners means that the milk does not suffer as easily from reflux and because gastric emptying occurs more rapidly.
4. Formulas for babies with lactose intolerance
Lactose is composed of two sugars that have to be separated by an enzyme present in the body, the lactase, in order to be absorbed. However, there may be situations where this enzyme is non-existent or insufficient, causing colic and diarrhea. Lactose intolerance is very common in babies because their gut is still immature.
To do this, one should opt for infant formulas without lactose, in which the lactose has been degraded into simpler sugars, which can already be absorbed by the body, as is the case of Aptamil ProExpert without lactose or Enfamil O-Lac Premium.
5. Milk for babies with intestinal discomfort
Intestinal discomfort is very common in infants because the intestine is still immature, causing colic and constipation.
In these cases you should choose milks enriched with prebiotics , such as Neslac Comfort or Nan Confort, which in addition to favoring the presence of good bacteria to the intestine, also reduce colic and constipation.
6. Milk for premature babies
The nutritional needs of preterm infants are different from those of normal weight. In these cases, you will have to choose formulas adapted to this situation, until the doctor indicates the change to a suitable adapted milk, or that breastfeeding is possible.

How to use properly adapted milk
In addition to a correct choice of formula, it is important to take certain care in its preparation. The preparation of milk should therefore be done with pre-boiled water, always taking care to cool the water before preparation, so as not to burn the baby's mouth or destroy the probiotics present in milk.
The bottle and the nozzle should also be washed and sterilized and the dilution of the powder in the water should be done exactly as recommended on the package. Here's how to wash and sterilize the bottle properly.
The World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding up to the 6th month of life as the sole source of infant feeding.