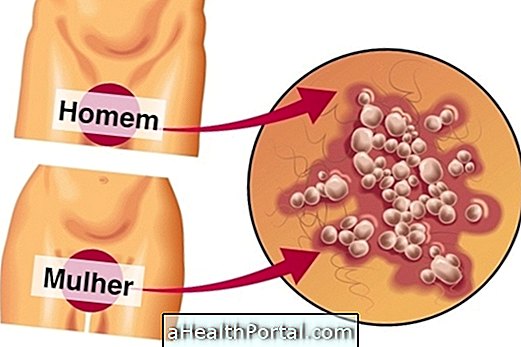
The lump in the vagina, which may also be known as a lump in the vagina, is almost always the result of an inflammation of the glands that help lubricate the vaginal canal, known as the Bartholin and Skene glands. sign of a serious problem, since this inflammation passes by itself.
However, if the lump causes symptoms like itching, burning or pain it may indicate other problems that need medical treatment, such as varicose veins, herpes or even cancer.
Therefore, whenever there is a change in the vaginal region, which takes more than 1 week to disappear or causes a lot of discomfort, the gynecologist should be consulted to identify the cause and initiate appropriate treatment.

1. Ingrown hairs or folliculitis
Women who do intimate waxing with wax, tweezers or a blade have an increased risk of developing ingrown hair in the region, which can result in a small reddish spine or itchy bone that hurts. Usually, this type of lump also presents a whitish central region, due to the accumulation of pus under the skin.
- What to do : You should expect the pus to be reabsorbed by the body and you should never burst the spine because it increases the risk of an infection. To relieve the symptoms you can apply a hot compress in the region and avoid wearing tight panties. If the pain worsens or the area becomes very hot or swollen, you should see your gynecologist to see if you need to use an antibiotic ointment.
2. Spine in the vagina, large or small lips

Although not very common, the spine can appear large and inflamed in the region of the vulva, groin, the entrance of the vagina or the large or small vaginal lips causing pain and discomfort.
- What to do: You should not try to squeeze the spine into the groin or use any remedy or cosmetic without the medical knowledge. Thus, it is necessary to go to the gynecologist for him to see and indicate the most indicated treatment. In some cases it may be necessary to use a corticosteroid-based ointment, such as candicort, for example, and make a bath using rosin, which has analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. In the most severe cases one can use the Trok N ointment and some antibiotic, like cefalexina.
3. Boil
The boil is an infection caused by bacteria and causes pain and intense discomfort. It may also arise in the groin, the large lips or the entrance of the vagina, initially with a ingrown hairs, which gave rise to the entrance of bacteria that have proliferated causing symptoms.
- What to do: The treatment is done with warm compresses and use of antibiotic ointments like Ictiol, for example, to prevent the furuncle from becoming an abscess, which is a bigger and very sore lump, in which case the doctor can indicate the take antibiotics in the form of tablets or make a small local cut to eliminate all contents.
4. Inflammation of the glands of Bartholin or Skene
In the vulva there are several types of glands that help to keep the region lubricated and with fewer bacteria. Two of these glands are the Bartholin glands, which when they ignite give rise to a Bartholinite, and the Skene glands.
When these glands are inflamed due to the presence of bacteria or poor hygiene, for example, a lump may appear in the external region of the vagina which, while not causing pain, may be palpated by the woman during the bath or sensing during intimate contact.
- What to do : in most cases the inflammation of these glands disappears after a few days maintaining the proper hygiene of the region. However, if the swelling increases or if pain or discharge of pus arises it is advised to go to the gynecologist, as it may be necessary to start using anti-inflammatories, antibiotics or analgesics, for example. Understand more about the treatment of inflammation of the Bartholin glands and the Skene glands.

5. Vaginal cyst
Vaginal cysts are small pockets of air or fluid that may develop on the walls of the vaginal canal and are usually caused by lesions during intimate contact or fluid accumulation in the glands, for example. Generally, they do not cause symptoms but can be felt as lumps or lumps inside the vagina.
A very common type of vaginal cyst is the Gartner's cyst which is most common after pregnancy and which arises due to fluid accumulation inside a canal that develops during gestation. This channel usually goes away in the postpartum, but in some women it can stay and ignite. Learn more about this type of cyst.
- What to do : Vaginal cysts usually do not need a specific treatment, and it is only recommended to monitor their growth with routine exams at the gynecologist.
6. Varices on the vulva
Although they are rarer, varicose veins may also develop in the genital region, especially after delivery or with natural aging. In these cases, the lump may show a slightly purple coloration and, although not causing pain, may cause a slight itching, tingling or discomfort sensation.
- What to do : In the case of the pregnant woman, treatment is usually not necessary, as varicose veins tend to disappear after delivery. In other cases, if you are disturbing the woman, the gynecologist can advise a minor surgery to close the vial and correct the varix. See treatment options for varicose veins in the pelvic region.
7. Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted disease that can be acquired through intimate oral, genital or anal unprotected contact. Other symptoms include fever, genitals and itchy feeling. These symptoms may disappear and reoccur later, especially when the immune system is weakened.
- What to do : There is no specific treatment for genital herpes because the virus needs to be combated by the immune system. However, when the symptoms are very intense, the gynecologist may advise the use of an anti-viral such as Aciclovir or Valaciclovir, for example. See also what care to have with genital herpes.

8. Genital Warts
Genital warts are also a type of sexually transmitted disease that can go through unprotected intimate contact. In these cases, in addition to small lumps in the vagina can also appear visible lesions similar to cauliflower, which can cause itching or burning.
- What to do : There is no cure for genital warts, but the doctor can remove the warts through some forms of treatment such as cryotherapy, microsurgery or acid application, for example. Understand the various ways to treat genital warts.
There are also other causes for the appearance of a lump, ball or spine in the groin or vagina and it is always advised to go to the doctor so that when observing the type of injury and other symptoms that may be present, reach the conclusion of what can be and of how the treatment can be done to eliminate any type of wound.