Hydatidosis is an infectious disease caused by the parasite Echinococcus granulosus which can be transmitted to humans through ingestion of water or food contaminated with feces from dogs infected by the parasite.
In most cases, hydatidosis takes years before the first symptoms appear and when they occur they are usually related to the location of the body where the parasite is present, occurring more frequently in the lung and liver. Thus, the symptoms that are usually related to hydatidosis are shortness of breath, frequent nausea, swelling of the belly or excessive tiredness.
Although there is treatment with antiparasitic drugs, some cases need to be treated with surgery to remove the parasites that are growing in the body and, therefore, the best way to eliminate the disease is to prevent infection with simple measures such as deworming all domestic dogs, washing hands before eating and preparing food correctly.

Main symptoms
The symptoms of hydatidosis can vary according to the location where the hydatid cyst is formed, and there may be different symptoms, the main ones being:
- Liver: is the main form of hydatidosis and is characterized by the presence of symptoms such as constant poor digestion, abdominal discomfort and swelling in the belly;
- Lungs: it is the second most frequent form of the disease and produces symptoms such as shortness of breath, easy tiredness and cough with phlegm;
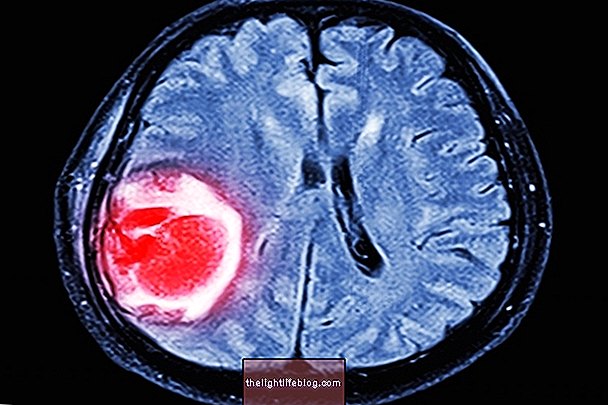
- Brain: happens when the parasite develops in the brain, leading to more serious symptoms such as high fever, fainting or coma;
- Bones: it is a rare form of the disease that can remain asymptomatic for several years, but which can also result in necrosis or spontaneous fractures.
In addition, when there is a rupture of the hydatid cyst, other complications can arise that can put the person's life at risk, such as pulmonary edema and anaphylactic shock, which is a type of severe allergic reaction. Understand what anaphylactic shock is and how to treat it.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The parasite develops slowly, which causes the disease to remain asymptomatic for several years, making diagnosis difficult. However, the presence of the parasite can be identified through routine examinations, such as X-rays, CT scans or ultrasounds, since the parasite forms cysts that can remain lodged in various organs.
Thus, the diagnosis of hydatidosis is made by the infectologist or general practitioner through the evaluation of signs and symptoms that may arise, imaging and laboratory tests, with the Casoni Reaction being the laboratory test used to confirm the diagnosis of hydatidosis, since identifies specific antibodies in the person's body.
Lifecycle of Echinococcus granulosus
The definitive host of Echinococcus granulosus it is the dog, that is, it is in the dog that there is the development of the adult worm, whose eggs are released into the environment through feces, contaminating food, children's hands and pastures, for example.
Eggs can remain viable in the soil for several months or years and are normally consumed by pigs, oxen, goats or sheep, where hydatid cyst develops in the liver and lungs, which can be consumed by dogs, especially in places where animals are bred for slaughter.
This disease is more frequent in children due to direct contact with dogs, for example, as the eggs may be attached to the hair. In addition, contamination can happen through the consumption of contaminated food and water, allowing the eggs to enter the body, transforming into an oncosphere in the stomach, impairing blood and lymphatic circulation and then reaching the liver, for example.
Upon reaching liver, lung, brain or bones, the oncosphere changes from hydatid cyst in a slow process that can last 6 months or more.
How the treatment is done
The treatment is carried out with the objective of eliminating parasites from the person's body and eliminating the parasite's cysts, and the use of antiparasitic agents, such as Mebendazole, Albendazole and Praziquantel, is normally recommended by the doctor, as they work to eliminate the parasite.
In some cases, surgical removal of the cyst may also be indicated, especially when it is very bulky and present in an easily accessible location. In this way, it is possible to avoid the cyst rupture and complications.
How to prevent hydatidosis
The prevention of infection by Echinococcus granulosus can be done through simple measures such as:
- De-worming all dogs, to reduce the likelihood of contagion;
- Ingest only treated water;
- Wash your hands after contacting dogs;
- Do not handle food without washing your hands;
- Always wash kitchen utensils after being used with raw vegetables.
In addition, it is important to avoid consuming raw vegetables from unknown sources, and when ingesting make sure that they have been properly sanitized, as well as it is important to wash your hands whenever you come into contact with animals and before preparing food.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- ZEIBIG, Elizabeth A. Clinical Parasitology. 2nd ed. United States of America: Elsevier, 2013. 256-259.
- MINISTRY OF HEALTH. Human hydatidosis (echinococcosis): causes, symptoms, treatment, diagnosis and prevention. Available in: . Accessed on 03 Jul 2020