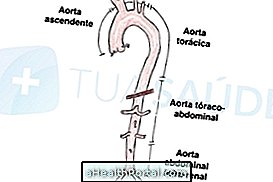
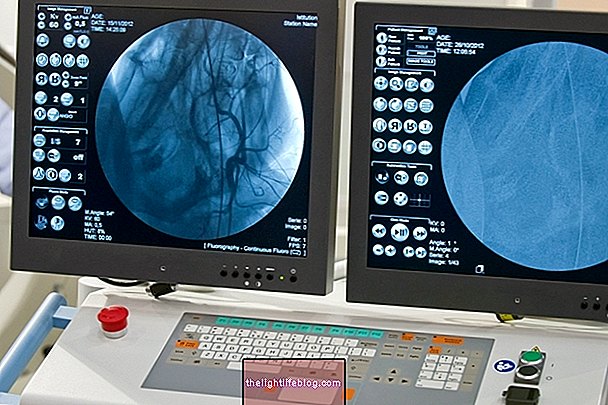
Cholangiography is an X-ray exam that serves to assess the bile ducts, and allows you to view the path of bile from the liver to the duodenum.
Often this type of examination is done during surgery on the bile ducts to remove a gallbladder stone, for example, but it can also be indicated by the doctor to help diagnose other problems related to the bile ducts, such as:
- Bile duct obstruction;
- Injuries, strictures or dilation of the ducts;
- Gallbladder tumor.
In addition, if an obstruction of the bile ducts is found, the doctor may, during the examination, remove what is causing the obstruction, causing an almost immediate improvement in symptoms.

How the exam is done
There are several types of cholangiography that can be ordered according to the doctor's suspicion.Depending on the type, the way of taking the exam may be a little different:
1. Intravenous cholangiography
This method consists of administering a contrast in the bloodstream, which will then be eliminated by the bile. After that, images are obtained every 30 minutes, which will allow the study of the contrast pathway through the bile ducts.
2. Endoscopic cholangiography
In this technique, a probe is inserted from the mouth to the duodenum, where the contrast product is administered and then an X-ray is made at the site of the contrast.
3. Intraoperative cholangiography
In this method, the examination is done during gallbladder removal surgery, called cholecystectomy, in which a contrast product is administered and several X-rays are performed.
4. Magnetic resonance cholangiography
This technique is performed after gallbladder removal surgery, with the objective of evaluating the bile ducts after removal, in order to identify possible complications that may be caused by residual stones not detected during the surgery.
How to prepare for the exam
Preparation for cholangiography may vary according to the type of examination, however, general care includes:
- Fast from 6 to 12 hours;
- Drink only small sips of water up to 2 hours before the exam;
- Inform the doctor about the use of medications, especially aspirin, clopidogrel or warfarin.
In some cases, the doctor may also order a blood test up to 2 days before the test.
Possible side effects
Although it is not very common, there are some side effects that can occur due to the performance of this test such as damage to the bile ducts, pancreatitis, internal bleeding or infection.
After cholangiography, if symptoms such as fever above 38.5ºC or abdominal pain that does not improve, it is advisable to go to the hospital.
When the exam should not be done
Although this test is considered safe, it is not recommended for people who have hypersensitivity to contrast, infection of the biliary system or who have high levels of creatinine or urea. In such cases, the doctor may recommend another test to assess the bile ducts.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- Anderson Fernandes Morais (organization). Didactic Course in Radiology. Vol. 2. São Caetano do Sul, SP: Yendis Editora, 2012. 89-94.
- CANCER RESEARCH UK. Cholangiography. Available in: . Accessed on 30 Oct 2020
- Maria Justina Ascensão Carvalho. Image Quality in Cholangio-pancreatography in Magnetic Resonance after Consumption of Black Tea. Conclusion work on the Master's Degree in Radiation Applied to Health Technologies, 2018. Instituto Politecnico de Lisboa.



-o-que--como-identificar-e-o-que-fazer.jpg)