Sexually transmitted diseases in humans usually cause symptoms such as itching and discharge in the penis, the appearance of warts or wounds in the intima and burning sensation when urinating.
To identify this type of disease and prevent complications, men with active sex life should go to the urologist at least once a year, so that the reproductive tract is evaluated and diseases treated promptly.

The main symptoms related to sexually transmitted diseases in humans are:
1. Itching, redness and pain in the penis
These symptoms are usually indicative of fungal infection, mainly by the fungus Candida albicans, which can be acquired during intimate contact, for example. This fungus can also develop in the mouth due to unprotected oral sex and causes symptoms such as sore throat, bad breath or whitish plaques on the cheeks, gums and throat.
In addition to Candidiasis, these symptoms may be indicative of genital herpes, which is a very common type of STD, which, in addition to these symptoms, is characterized by the presence of small blisters and small sore wounds in the intima
How to treat: In the case of Candidiasis, treatment is usually done with the application of creams or ingestion of antifungal medicines, such as Fluconazole or Clotrimazole, which should be recommended by the urologist. In the case of genital herpes, the urologist may recommend the use of antiviral drugs or the application of ointments such as Aciclovir or Fanciclovir, for example, that should be used for 10 to 14 days or as directed by your doctor. Find out what care you should take during treatment for genital herpes.
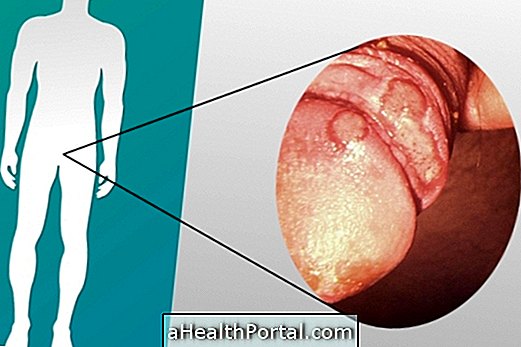
2. Wounds in the genital organ
The presence of wounds, lumps, or blisters on the genital organ usually occurs due to infection by a microorganism during sexual contact and is therefore indicative of an STD.
HPV, which is a disease caused by the Human Papilloma Virus, is characterized by the presence of warts on the penis, scrotum or anus, but may also be present in the mouth or throat if these regions have been in contact with the secretions of the infected partner or partner .
Other diseases that may be characterized by the presence of small wounds or blisters in the genital area are genital herpes and syphilis, which is characterized by the presence of intimately injured wounds that do not hurt, as well as lumps in the neck that cause pain and result in pain headache, general malaise and fever.
How to treat: Treatment for genital herpes is done with the use of antiviral drugs according to the urologist's guidance. In the case of HPV, the doctor may recommend the application of ointment to eliminate the wart, such as Podofilina, and the virus is eliminated naturally from the body.
The treatment for syphilis depends on the stage of the disease, and it is usually recommended by the physician to apply a penicillin injection in the early stages and, in the later stages, several injections may be necessary. See more about how syphilis is treated.
3. Grief
The presence of discharge may also be indicative of STD, especially Gonorrhea or Chlamydia . In the case of Gonorrhea, it can be noticed the presence of yellowish discharge similar to pus, besides pain and burning when urinating and low fever. If there has been oral or anal contact with the infected person, throat pain and inflammation of the anus, for example, may occur.
Chlamydia is also an STD characterized by the presence of discharge in the penis, but there may also be pain when urinating and swelling in the testicles.
How to treat: These STDs are caused by bacteria, so usually a urologist indicates the use of antibiotics such as Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone or Erythromycin for about 1 week or as directed by your doctor. It is important that the treatment of Chlamydia be performed according to the doctor's advice, because if it is not treated in the correct way, it can result in infertility. Learn more about Chlamydia treatment.
4. Pain and burning on urination
Pain and burning when you urinate are usually symptoms of urinary tract infections, but may also be indicative of sexually transmitted diseases, such as genital herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and candidiasis, for example.
How to treat: In these cases, it is important to go to the urologist to be asked for tests to identify the cause and, thus, to start the treatment, which can be done with antiviral drugs, antibiotics or antifungal medicines.
5. General malaise, weight loss and mouth sores
Not always the symptoms of STD are related to changes in the genital region, is the case of HIV infection, whose initial symptoms are similar to influenza, such as fever, malaise and headache. In addition, there may be high and persistent fever, rapid weight loss, tiredness, diarrhea, red spots on the skin and mouth sores.
How to treat: HIV infection has no cure; however, it can be controlled by ingestion of antiviral drugs to prevent the progression of infection, the occurrence of AIDS, or the onset of some complications. Know which remedies are used in the treatment.