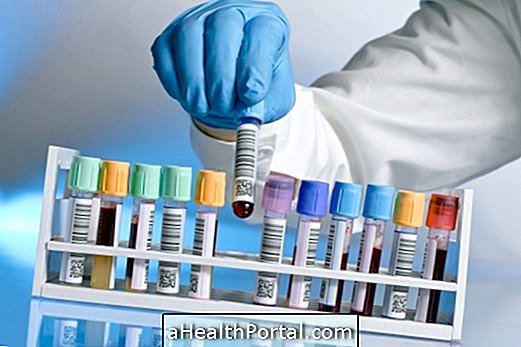
The T3 test is requested by your doctor after abnormal results of TSH or T4 hormone or when the person has signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism such as nervousness, weight loss, irritability, and nausea. Learn how to identify hyperthyroidism.
The hormone TSH is responsible for the stimulation of T4 production, mainly, which is metabolized in the liver in order to give rise to its most active form, T3. Although most T3 is derived from T4, the thyroid also produces this hormone, but in smaller amounts. Find out what it is for and how the T4 exam is done.
It is not necessary to fast for the test, however, some medicines may interfere with the test result, such as thyroid medicines and contraceptives, for example. Therefore, it is important to tell the doctor so that guidance can be given regarding the safe suspension of the drug for the test.
What is it for
The T3 test is required when the TSH and T4 test results are changed or when the person has symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Because it is a hormone normally found in low blood concentrations, T3-only dosing is not widely used to assess thyroid function and is usually required when the diagnosis of thyroid abnormality is confirmed or together with TSH and T4 . See which tests evaluate the thyroid.
In addition to being useful to aid in the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, the T3 test may also be requested to help identify the cause of hyperthyroidism, such as Graves' disease, for example, and is usually ordered together with the thyroid autoantibody dosage. Know what Graves' disease is and how to treat it.
The test is done from a blood sample sent to the laboratory, where the concentration of total T3 and free T3, which corresponds to only 0.3% of the total T3, is measured, being thus more found in its conjugated form to proteins . The reference value of total T3 is between 80 and 180 ng / dL and free T3 is between 2.5 - 4.0 ng / dL and may vary according to the laboratory.
How to understand the result
T3 values vary according to the health of the person, and may be increased, decreased or normal:
- High T3: Normally confirms the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, being indicative of Graves' disease, mainly;
- T3 low: It may indicate Hashimoto's thyroiditis, neonatal hypothyroidism or secondary hypothyroidism, and complementary tests are necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
The results of the T3 test, as well as that of T4 and TSH, only indicate that there is some alteration in the production of the hormones by the thyroid, and it is not possible to determine the cause of this dysfunction. Therefore, your doctor may order more specific tests to identify the cause of hypo or hyperthyroidism, such as a blood count, immunological and imaging tests.
What is Reverse T3?
Reverse T3 is the inactive form of the hormone derived from the conversion of T4. Reverse T3 dosing is not required, and is indicated only for patients with serious diseases involving the thyroid, with decreased levels of T3 and T4, but high levels of reverse T3. In addition, reverse T3 may be elevated in situations of chronic stress, HIV infection, and renal failure.
The reference value of Reverse T3 for newborns is between 600 and 2500 ng / mL and from the 7th day of life, between 90 and 350 ng / mL, and may vary between laboratories.