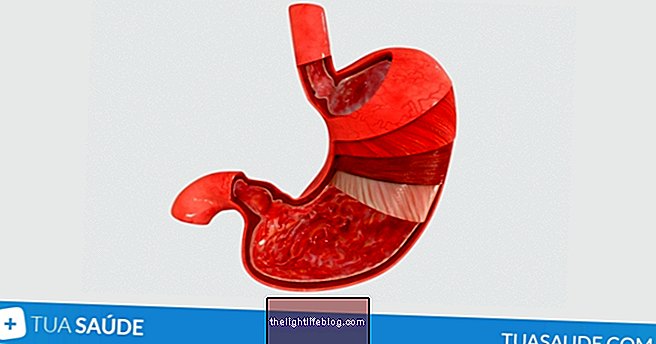
Caroli syndrome is a rare hereditary disease that affects the liver, which was named after the French physician Jacques Caroli who discovered it in 1958. It is a disease characterized by dilatation of the channels that carry the bile, generating pain due to inflammation these same channels. It can produce stones and infection, and may be associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis, which is a more severe form of the disease.
Symptoms of Caroli's Syndrome
The symptoms of Caroli's syndrome are:
- Acute pain due to inflammation of the bile ducts and presence of stones;
- Jaundice;
- Fever;
- Abdominal pain;
- Generalized burning;
- Liver growth.
The disease can manifest at any time in life and can affect several family members, but it is inherited recessively, which means that both the father and the mother have to be carriers of the altered gene.
Diagnosis of Caroli's syndrome
The diagnosis of Caroli syndrome can be made by performing examinations such as magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
Treatment for Caroli's syndrome
Treatment for Caroli syndrome involves taking antibiotics, surgery to remove stones, and if the disease affects only one liver lobe, extraction may be necessary as well as a liver transplant in some cases.