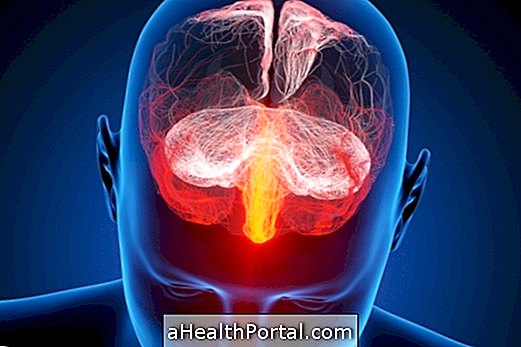
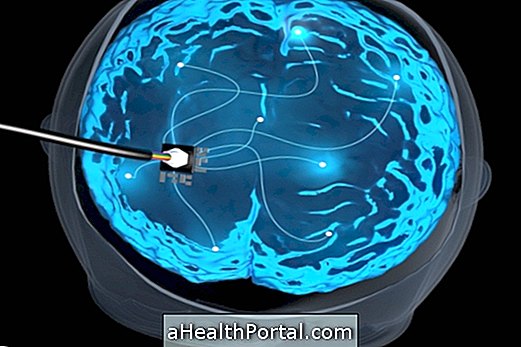
Deep Brain Stimulation, also known as a brain pacemaker or DBS, is a surgical procedure in which a small electrode is implanted to stimulate specific regions of the brain.
This electrode is attached to a neurostimulator, which is a kind of battery, which is implanted under the scalp or in the region of the clavicle.
This surgery, which is done by the neurosurgeon, has caused an improvement in many neurological diseases, such as Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, epilepsy and some psychiatric diseases, such as depression and OCD, but it is only indicated for cases in which there was no improvement with medication use.
The main diseases that can be treated are:
1. Parkinson's disease
The electrical impulses of this technique stimulate regions in the brain, such as the subthalamic nucleus, that help control movements and improve symptoms such as tremor, stiffness and difficulty walking, and therefore, Parkinson's disease is the disease most treated by stimulation surgery cerebral palsy.
Patients undergoing this therapy may also benefit from improved sleep, swallowing of foods and smell, which are detrimental to the disease. In addition, it is possible to decrease the dose of the medicines used and avoid their side effects.
2. Dementia of Alzheimer
Deep brain stimulation surgery has also been tested and used to try to regain Alzheimer's symptoms, such as forgetfulness, difficulty in reasoning and behavior change.
In the initial results, it has already been observed that the disease is stationed longer and, in some people, its regression could be noticed due to better results presented in the reasoning tests.
3. Depression and OCD
This technique has already been tested for the treatment of severe depression, which does not improve with the use of medication, psychotherapy and electroconvulsive therapy, and it can stimulate the region of the brain responsible for improving mood, which reduces the symptoms in most patients who have already done this therapy.
In some cases, with this treatment, it is also possible to reduce the compulsive and repetitive behavior that exists in OCD, in addition to being a promise to reduce the aggressive behavior of some people.
4. Movement Disorders
Diseases that cause changes in movement and cause involuntary movements, such as essential tremor and dystonia, for example, have great results with deep brain stimulation, because, just like in Parkinson's, regions of the brain are stimulated for movement control, in those who do not improve with the use of medicines.
Thus, one can already notice the improvement in the quality of life of many people who did this therapy, mainly, by allowing to walk more easily, to control the voice and to be able to carry out some activities that were no longer possible.
5. Epilepsy
Although the region of the brain affected by epilepsy varies according to its type, the frequency of seizures has already been demonstrated in people who have had therapy, which makes treatment easier and reduces the complications of people suffering from epilepsy. disease.
6. Eating Disorders
The implantation of the neurostimulator device in the region of the brain responsible for appetite can treat and lessen the effects of eating disorders such as obesity, lack of appetite control, and anorexia in which the person stops eating.
Thus, in cases where there is no improvement with treatment with medication or psychotherapy, deep stimulation therapy is an alternative that promises to help in the treatment of these people.
7. Addictions and addictions
Deep brain stimulation seems to be a good promise for treating people who are addicted to chemicals, such as illicit drugs, alcohol or cigarettes, which can make addiction lessened and avoided.

Price of deep brain stimulation
For this surgery you need expensive material and a very specialized medical team, which can cost around R $ 100, 000.00, depending on the hospital performed. Some selected cases, when referred to hospitals where this technique is available, can be performed by SUS.
Other benefits
This therapy can also bring improvements to the recovery of people who have suffered from a stroke and can reduce the sequelae, alleviate chronic pain and even help in the treatment of La Tourette syndrome, in which the person has uncontrollable motor and vocal tics.
In Brazil, this type of surgery is only available in large hospitals, especially in capitals or large cities, where neurosurgery centers are equipped. As it is an expensive procedure and little available, this therapy has been reserved for people with serious diseases and who do not respond to the treatment with medicines.