Crohn's disease is a chronic disorder of the digestive system that causes a chronic inflammation of the lining of the intestines. Thus, one of the most characteristic symptoms is the urgent need to defecate, with severe diarrhea that may contain mucus or blood, and is usually accompanied by headache and fever below 38º C.
If you think you may have this disease, select your symptoms and find out what the odds are:
- 1. Periods of severe diarrhea with mucus or blood Yes No
- 2. Urgent urge to defecate, especially after eating Yes No
- 3. Frequent abdominal cramps Yes No
- 4. Nausea or vomiting Yes No
- 5. Loss of appetite and weight loss Yes No
- 6. Persistent low fever (between 37.5º and 38º) Yes No
- 7. Lesions in the anal region such as hemorrhoids or fissures Yes No
- 8. Frequent tiredness or muscle pain Yes No

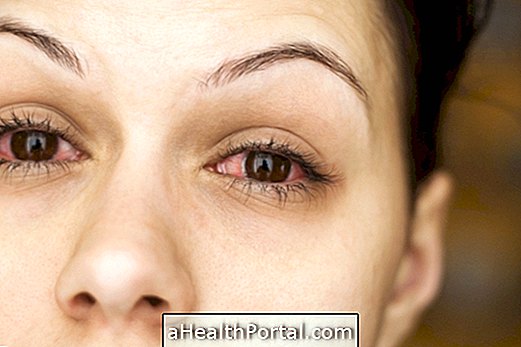
In addition, this disease can also affect the eyes, leaving them inflamed, red and sensitive to light, and may also increase the risk of colon cancer.
This is a difficult disease to identify that can take months or years to manifest the first symptoms and therefore, some people may only present one or two of these symptoms for some time without being suspicious of Crohn's disease. See the possible causes of Crohn's disease.

How to confirm the diagnosis
When some of these symptoms appear, it is advisable to go to the gastroenterologist to have a colonoscopy, which is an examination that allows you to observe the walls of the intestine to assess the presence of inflammation. If it is not possible to observe alterations in the intestine, it is common for the doctor, during colonoscopy, to remove a small sample of the intestinal wall to make a biopsy in the laboratory, and to confirm the diagnosis.
How is the treatment done?
Crohn's disease has no cure, so changes in eating habits are very important in order to reduce the symptoms, since certain foods can cause or aggravate the crisis of the disease. Thus, it is recommended to control the amount of fiber ingested, reduce the amount of fats and limit the consumption of milk derivatives. In addition, it is very important to bet on daily hydration in order to avoid dehydration. Here's how to adapt the food to relieve the symptoms.
During crises, your doctor may also recommend taking some anti-inflammatory medicines to reduce pain and inflammation, as well as medicines that may help control diarrhea.
In the most severe cases of the disease, surgical intervention may be indicated to remove affected and damaged portions of the intestine that may be causing the symptoms.