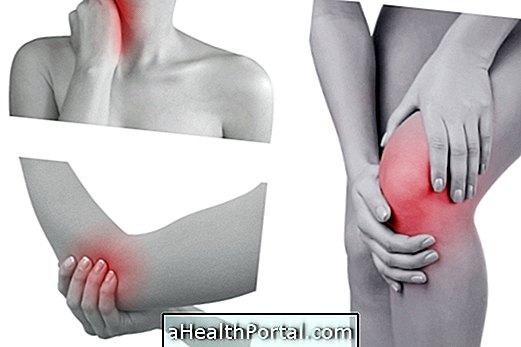
Arm pain may indicate changes in muscles, tendons, or cardiovascular changes, for example. In order to identify what is causing this symptom, it should be observed when the pain in the arm has arisen, its intensity, if it improves or worsens with rest, and it is possible to identify situations like strokes, pains in other parts of the body, for example.
Here are 10 possible causes of arm pain.
Main causes of arm pain
1. Infarction
Chest pain that can radiate to the arm, feeling heavy, and a tingling sensation in the left arm may indicate a heart attack. In some people the heart attack may not be so characteristic and manifest with a feeling of poor digestion and discomfort in the throat. Know all the symptoms of the infarction.
- What to do: You should go to the emergency room to be evaluated.
2. Angina:
Angina is chest pain that can sometimes radiate to the arm. This pain is related to circulatory changes such as atherosclerosis if they are fat plaques that build up inside the arteries throughout life, especially in people with high blood pressure and diabetes. Angina can arise after strong emotions or make some effort, for example.
- What to do: If a heart attack or angina is suspected, go to the emergency room. The doctor may recommend the use of medicines to improve blood flow through arteries such as dinitrate or isosorbide mononitrate, for example. Learn more details of the treatment of different types of angina.
3. Panic Attack or Anxiety Crisis:
An anxiety crisis can cause symptoms like shaking, heart palpitation, chest pain, hot feeling, sweating, shortness of breath and strange feeling in the arm. In a panic crisis the person may experience belly pain, diarrhea and may not be able to leave the house, avoiding contact with people, preferring to be alone in the room.
- What to do: In a crisis of panic or anxiety you should take a deep breath, stay calm and if need be, you can get crouched to feel more protected. Here's what else you can do to deal with a panic attack.
4. Tendonitis:
Arm and shoulder pain can be tendinitis, a situation that mainly affects teachers, servants and painters because they have to raise their arm several times a day to work. However the pain can also affect bus or truck drivers or people who have fallen and hit their shoulders on the ground. The pain can be located only on the shoulder or radiate also by the arm, reaching up to the elbow.
- What to do: Putting a cold compress with crushed ice is a good option to fight shoulder and arm pain. Physical therapy is also a good option for persistent pains that last for more than 1 month. Learn about treatment options and some exercises for shoulder tendinitis.

5. Distension in the biceps or triceps muscles:
The signs and symptoms of a strain on the muscle in the front or back of the arm are localized pain near the elbow, which may have arisen after a fall, stroke or strain in the gym, for example. The region may spin a little swollen, but this is not always noticeable.
- What to do: During the first 48 hours, it may be helpful to put a cold compress on the pain site, and after that time it is best to put on a warm compress for 20 minutes, 1 or 2 times a day. Passing an anti-inflammatory ointment like Diclofenac may also help. Learn more details on how you can treat a strain in your muscles.
6. After removal of the breast:
After surgery to remove the breast, it is normal for the arm to become swollen and sore, especially in the first few weeks. The pain can affect every arm, with a feeling of weight, tingling that reaches the hands. This is because the vessels of the lymphatic system, which removes the swelling may be compromised by surgery.
- What to do: Physical therapy has a number of features that can help with manual lymphatic drainage, with pressure therapy or tapes like Kinesio tape, which help in venous return, swelling the arm, and reducing pain. See more details on recovery from mastectomy.
7. Thoracic Gorge Syndrome:
In this syndrome besides arm pain, there is tingling or burning in the hands and fingers due to compression of the blood vessels, especially affecting people who have suffered a car accident or repetitive lesions in the thorax, but can also develop in pregnant women, reducing or disappearing after the childbirth.
- What to do: The doctor may recommend the use of pain relievers for pain relief, osteopathy sessions may be indicated to improve body alignment in order to decrease nerve compression, but in more severe cases when there is no improvement of symptoms with these strategies, even surgery can be indicated. Check out a few exercises that can help control this syndrome.
8. Shoulder displacement:
The pain in the arm and the shoulder may be in people who can easily dislocate the shoulder, doing this of their own volition. This can happen after an episode of involuntary shoulder movement. In this case, the person gets the capsule that forms the joint and ligaments more elastic than normal, facilitating the removal of the bone from the arm from inside the shoulder.
- What to do: To relieve the pain you can take a warm bath and pass an ointment like Diclofenac on the shoulder and arm. But to prevent this shift from occurring frequently it is advised to strengthen the muscles with shoulder exercises in the gym or physiotherapy. Learn how to identify and detail the treatment for shoulder dislocation.

9. Osteoporosis:
Pain in the arms and legs may indicate osteoporosis, this pain may be present even when you are at rest, being more common in people over 50, especially women during or after menopause.
- What to do: Treatment should be done with increased intake of calcium-rich foods and with medicines that supplement calcium and vitamin D, for example. See more tips in this video:

10. Nerve injury:
When there is pain in the arm, there is pain in the rib, intercostal neuralgia can be suspected, which happens mainly during pregnancy due to the growth of the belly. There may also be frequent sweating, muscle spasms, fever and a tingling sensation in the skin, which can be confusing with heart problems, increasing stress levels.
- What to do: Putting warm compresses at the pain site can help you feel more comfortable, resting on a firm mattress can also be indicated. The orthopedic doctor is the most suitable for this cause, and physiotherapy and osteopathy sessions may be necessary. B-complex supplementation may also be indicated because it improves nerve function, relieving pain.
When to go to the doctor
You should go to the emergency room if:
- Suspect of myocardial infarction or angina pectoris;
- If the pain in the arm arises suddenly and is very strong;
- When the pain gets worse with effort;
- If it seems that the pain is in the bones and finds no relief at all;
- If you notice any clear deformity in the arm.
You should see your doctor if:
- Have had arm pain for more than 1 week;
- Pain in the arm that radiates to the shoulder or hands or fingers;
- Severe pain and swelling in the arm;
- If the pain is getting worse over time.
If symptoms such as fever are present it is possible that it is caused by an infection, and it is necessary to perform tests to identify the cause.