Cerebral hemorrhage is a type of stroke, also called stroke, in which bleeding occurs around or inside the brain because of the rupture of a blood vessel, usually an artery of the brain. Learn more about hemorrhagic stroke.
It is a serious event, usually caused by a blow to the head, which can lead to a state of profound unconsciousness, as well as nausea, vomiting, decreased heart rate and loss of balance.
The diagnosis is made by imaging tests, such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance and angiography with or without contrast. In other cases the doctor may still request lumbar puncture.
The treatment of cerebral hemorrhage is usually surgical, and aims to remove blood and clot to lower the pressure inside the brain caused by bleeding.
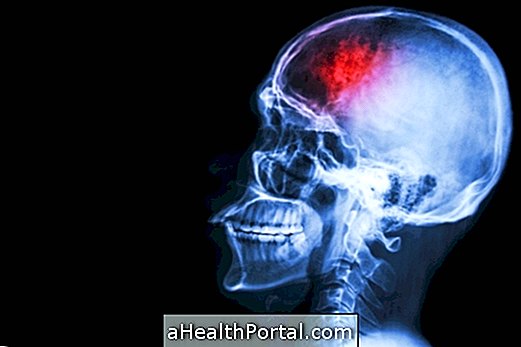
Main symptoms
The symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage depend on the size of the bleeding and are usually:
- Severe headache that can last for days;
- Numbness or tingling in any part of the body;
- Vomiting;
- Loss of balance;
- Trembling in hands;
- Decreased heart rate;
- Generalized weakness;
- Swelling of part of the optic nerve, which may result in dark vision for a few seconds, decreased vision or blindness;
In more severe conditions there may be sudden epileptic seizures or profound and prolonged loss of consciousness in which the person can not respond to stimuli.
Does brain hemorrhage leave sequelae?
After bleeding, some people may have sequelae, such as difficulty speaking, swallowing, walking, carrying out day-to-day activities or being paralyzed.
As soon as the onset of the first symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage occurs, one should go to the doctor promptly so that treatment can be initiated, as the severity of the sequelae depends on the degree of bleeding.
The best way to avoid the occurrence of cerebral haemorrhage and, consequently, its sequels, is to perform physical activities and have a healthy and balanced diet, low in fat and salt.
Causes of cerebral hemorrhage
The main cause of brain hemorrhage is head trauma, but there are other conditions that may favor bleeding, such as:
- High pressure;
- Genetic factors;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Use of drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamine;
- Amyloid angiopathy, which is the inflammation of small vessels in the brain;
- Blood diseases, such as thrombocythemia and hemophilia, that make the coagulation process difficult;
- Use of anticoagulants, as they make coagulation difficult, which may favor bleeding;
- Brain tumors.
Another common cause of cerebral hemorrhage is the aneurysm, which is dilation in a blood vessel. This dilation causes the walls of this vessel to become thin and fragile, and can rupture at any time, with bleeding.
The most common symptom of the aneurysm is headache. Some people report feeling their heads hot, as if there is some kind of leak. Learn more about the signs and treatment of brain aneurysm.

How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis is made by performing imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance, computed tomography and angiography with or without contrast.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows visualization of the edema around the lesion and, thus, the degree of lesion is known. Computed tomography is important so that the doctor can check for hemorrhage and thus differentiate the hemorrhagic stroke from ischemic stroke. See what causes stroke and how to avoid it.
Angiography is the diagnostic exam that facilitates the visualization of the interior of the blood vessels, being able to evaluate the form, presence of malformations and also to diagnose the aneurysm, for example. Understand how angiography is done and what angiography is for.
Some people with cerebral hemorrhage, however, present normal results on MRI or computed tomography. Therefore, the doctor may request a lumbar puncture, which is the removal of the cerebrospinal fluid from the hip bone, to be able to evaluate the CSF, since in the cerebral hemorrhage one has blood in the CSF.
How to treat
Treatment for cerebral haemorrhage is usually done with surgery to remove blood and clot and decrease the pressure inside the brain caused by bleeding.
In addition to surgery may be indicated by the doctor the treatment with medicines to control the pressure, seizures and possible infections. In more severe cases blood transfusions may also be indicated.
To improve the quality of life after bleeding in the brain and avoid injury it is important to go to the physiotherapist or occupational therapist. Here's what recovery is like after a stroke.

Main types of cerebral hemorrhage
Excess blood irritates the brain tissue and leads to the formation of edema, which is the accumulation of fluid. Excess blood and liquids increase pressure on brain tissue, slow the circulation of blood through the nervous system, and kill brain cells. Cerebral haemorrhage can be classified according to the location that occurs in:
1. Intraparenchymal or intracerebral hemorrhage
This type of bleeding is most likely to happen in the elderly and is when bleeding is inside the brain. It is the most serious type, but also the most common type in the population. It usually occurs due to tumors, coagulation disorders and malformed vessels.
2. Intraventricular hemorrhage
Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs in the cerebral ventricles, which are brain cavities in which cerebrospinal fluid production occurs. This type of bleeding usually occurs in preterm infants as early as 48 hours after birth, and has had some complications as soon as they are born, such as respiratory distress syndrome, in which the baby is born with immature lungs, high blood pressure, and pulmonary collapse, which is a respiratory complication in which there is not sufficient air passage. Learn more about lung collapse.
3. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
This hemorrhage usually occurs due to the rupture of an aneurysm, but may also be the result of a blow, and is characterized by bleeding into the space between two layers of the meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater.
The dura, arachnoid and pia mater are the constituent layers of the meninges, which are membranes that line and protect the central nervous system. Subarachnoid hemorrhage usually occurs in people between 20 and 40 years of age.
4. Subdural hemorrhage
Subdural hemorrhage occurs in the space between the dura mater and arachnoid layers of the meninges and is the most frequent result of trauma.
5. Epidural bleeding
This bleeding occurs between the dura and the skull and is more common in children and adolescents as a result of a fractured skull.