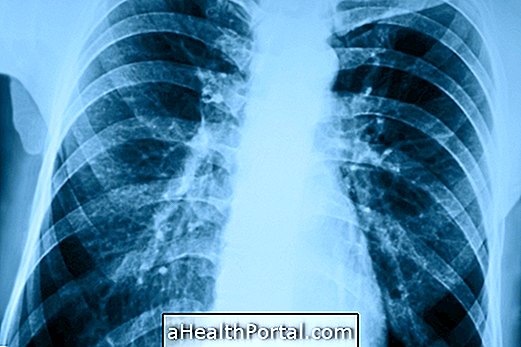
Pneumoconiosis is an occupational disease caused by the inhalation of chemicals such as silica, aluminum, asbestos, graphite or asbestos, for example, leading to respiratory problems and difficulties.
Pneumoconiosis usually occurs in people working in places where there is direct and constant contact with a lot of dust, such as coal mines, metallurgical factories or construction sites, and is therefore considered to be an occupational disease. Thus, while working, the person breathes in these substances and, over time, pulmonary fibrosis may occur, making lung expansion difficult and resulting in respiratory complications such as bronchitis or chronic emphysema. Get to know other diseases that can arise at work.

Types of pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is not an isolated disease, but several diseases that may present more or less the same symptoms but differ by cause, ie by inhaled powder or substance. Thus, the main types of pneumoconiosis are:
- Silicosis, in which excess silica dust is inhaled;
- Anthracosis, also called black lung, in which coal dust is inhaled;
- Beryliosis, in which there is constant inhalation of beryllium dust or gases;
- Bissinosis, which is characterized by the inhalation of dust from cotton fibers, flax or hemp;
- Siderosis, in which there is excessive inhalation of dust containing iron particles. When silica particles are inhaled in addition to iron, this pneumoconiosis is called Siderosilicosis.
Usually pneumoconiosis does not cause symptoms, however if the person has constant contact with these potentially toxic substances and presents with dry cough, difficulty breathing or tightness in the chest, it is recommended to seek medical help for tests and to diagnose pneumoconiosis.
Companies are required by law to carry out examinations at the time of admission, prior to dismissal and during the person's contract period for any work-related illness, such as pneumoconiosis. Thus, it is recommended that people working in these conditions perform at least 1 consultation with the pulmonologist per year to verify their health status. See which are the admission exams, periodicals and exams.
How to avoid
The best way to avoid pneumoconiosis is by using a well-fitted face mask at work to avoid inhaling chemicals that cause the disease, as well as washing your hands, arms and face before going home.
However, the workplace should also provide favorable conditions, such as having a dust-inducing ventilation system and places to wash hands, arms and face before leaving work.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for pneumoconiosis should be guided by a pulmonologist, but usually includes the use of corticosteroids, such as Betamethasone or Ambroxol, to reduce symptoms and facilitate breathing. In addition, the person should avoid being in very polluted places or with dust.










.png)


