The hypoechoic or hypoechogenic nodule is one that is visualized through imaging tests such as ultrasonography and indicates a lesion of low density, usually formed by liquids, fat or very dense tissues, for example.
Being hypoechoic does not confirm whether the lump is malignant or benign, because in the ultrasound examination the word "echogenicity" indicates only the ease with which the ultrasound signals pass through the structures and organs of the body. Thus, hyperechoic structures tend to have a higher density, while hypoechoic or anechoic structures have little or no density.
Nodules are lesions formed by the accumulation of tissues or liquids that measure more than 1 cm in diameter and are generally rounded and similar to lumps. They can have the following characteristics:
- Cyst : arises when the lump has liquid contents inside. Check out the major types of cyst and when they can be serious;
- Solid : when its contents contain solid or thick structures, such as tissues, or a liquid that has a considerable density, with many cells or other elements in it;
- Mixed : may arise when the same nodule encompasses solid and liquid structures in their contents.
A lump may appear on the skin, subcutaneous tissue or any other organ in the body, and it is common to be detected in the breast, thyroid, ovaries, uterus, liver, lymph nodes, or joints, for example. Sometimes, when superficial, they can be palpated, while in many cases, only ultrasound or CT scans can detect.
When is the nodule severe?
Usually, the nodule presents characteristics that may indicate that they are serious or not, however, there is no rule for all, and the doctor's evaluation is necessary to observe not only the result of the examination, but also the physical examination, the presence of symptoms or risks that the person may present.
Some characteristics that may raise suspicion of the nodule vary according to the organ in which it is located, and can be:
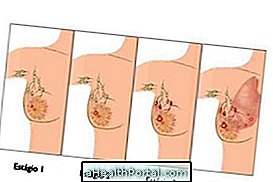
1. Hypoechoic nodule in the breast
Most often, the lump in the breast is not of concern, and benign lesions such as fibroadenoma or simple cyst usually appear. A cancer is usually suspected when there are changes in the size or shape of the breast, in the presence of a family history, or when the lump shows signs of malignancy, such as being hard, adhering to neighboring tissues or having many blood vessels, for example.
However, if a tumor is suspected in the breast, the doctor will indicate a puncture or biopsy to determine the diagnosis. See more on how to know if the breast lump is malignant.
Hypoechoic nodule in the thyroid
The fact that it is hypoechogenic increases the chances of malignancy in a thyroid nodule, however, only this feature is not enough to determine if it is a cancer or not, requiring medical evaluation.
In most cases, the tumor is usually punctured when it reaches more than 1 cm in diameter, or 0.5 cm when the nodule has malignant characteristics, such as the hypoechoic nodule, presence of microcalcifications, enlargement of the blood vessels, infiltration in the neighboring tissues or when it is taller than wide in transverse view.
Nodules should also be punctured in people at high risk for malignancy, such as those who had exposure to radiation in childhood, who have genes associated with cancer or who have a personal or family history of cancer, for example. However, it is important for the physician to evaluate each case individually, as there are specificities and the need to calculate the risk or benefit of the procedures, in each situation.
Learn how to identify the lump in the thyroid, what tests to do, and how to treat.
3. Hypoechoic nodule in the liver
Hepatic nodules have variable characteristics, so the presence of a hypoechoic nodule is not sufficient to indicate whether it is benign or malignant, requiring the physician to make an assessment in more detail, in each case, to determine.
Usually, the lump in the liver is investigated for the presence of malignancy with imaging tests, such as tomography or resonance, whenever it is larger than 1 cm or when it presents constant growth or change of appearance. In some cases, the doctor may indicate a biopsy to confirm whether or not the lump is severe. Know when the liver biopsy is indicated and how it is done.
How is the treatment done?
The hypoechoic nodule does not always have to be removed because, in most cases, it is benign and requires observation only. The doctor will determine how often the nodule will be followed, with tests such as ultrasound or CT scan, for example, which can be every 3 months, 6 months or 1 year.
However, if the nodule develops suspicion of malignancy, such as rapid growth, adherence to neighboring tissues, changes in characteristics or even when it becomes very large or causes symptoms, such as pain or compression of nearby organs, it is indicated the performance of a biopsy, a puncture, or a surgery to remove the lump. Learn how breast lift surgery is done and how recovery is done.