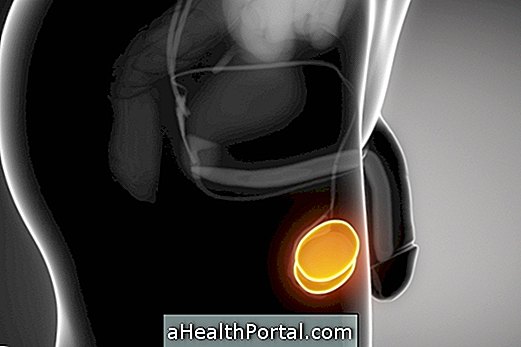
Myoma is a kind of a benign tumor consisting of muscle tissue and fibrous tissue that grows in the wall of the uterus that normally grows faster during pregnancy and menopause.
The severity and need for removal is determined by the gynecologist.
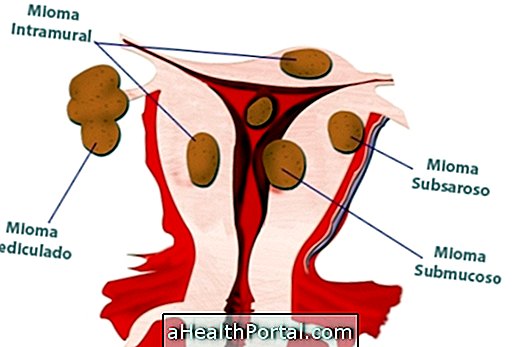
There are 3 types of uterine fibroid and they can develop inside, outside, between the walls of the uterus or inside the uterine cavity. They can be classified into 3 types: subserosal, intramural or submucosal.
- Subserous myoma : It is located outside the walls of the uterus and is nourished by a blood vessel (vascular pedicle) and therefore can be called pediculate.
- Intramural Myoma : It is located between the walls of the uterus.
- Submucous Myoma : It is located on the inner wall of the uterus and may affect the endometrium.
The submucosal fibroids are the ones that most interfere with fertility and menstrual disorders, usually the others do not generate symptoms.
Symptoms of uterine fibroid
The symptoms of uterine fibroids can be:
- Abdominal pain;
- Increased abdominal volume;
- Severe cramping during menstruation;
- Pain during intercourse;
- Menstruation abundant;
- Loss of blood outside the menstrual period;
- Increased urge to urinate due to pressure on the bladder.
However, there are women who have no symptoms and are found on a routine examination.
Treatment for uterine fibroid
Treatment for uterine fibroids can be done by taking hormonal medications or surgery, depending on the severity of the symptoms and their location.