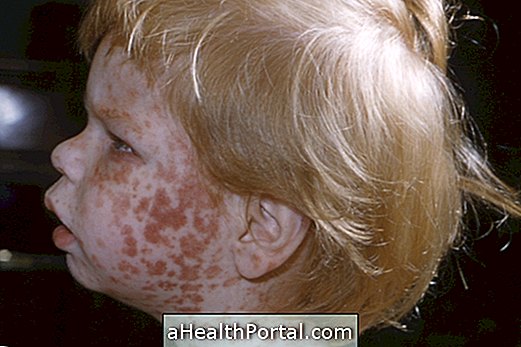
Rubella is a contagious disease, which is usually not serious, but causes symptoms such as itchy red patches that initially appear on the face and behind the ear and then go all over the body toward the feet.
The first symptoms of rubella are similar to flu and manifest through low fever, red and watery eyes, cough and nasal discharge. After 3 to 5 days red spots appear on the skin that last about 3 days.
Thus, the characteristic symptoms of rubella are:
- Fever up to 38ºC;
- Nasal discharge, cough and sneezing;
- Headache;
- Malaise;
- Increased ganglia, especially near the neck;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Red spots on the skin that cause itching.
The stage of greatest risk of infection involves the 7 days before the onset of the blotches on the skin and lasts up to 7 days after they appear.
The symptoms of rubella during pregnancy and in babies who have been contaminated after birth are the same observed at any stage of life. However, when the mother is infected during pregnancy, the baby can be severely affected.
How to know if it is rubella
The diagnosis usually consists of the physical evaluation of the person, in which the doctor examines the person's skin for rashes and evaluates other characteristic symptoms of the disease, such as white spots on the mouth, fever, cough and sore throat.
To know if the person is with rubella, one must observe the symptoms that it presents, verifying if it took the triple viral vaccine that protects of this disease. If it has not been vaccinated, the doctor may order a blood test that identifies antibodies formed against the Rubivirus, which causes Rubella. Although not frequent, some people who have taken the triple viral vaccine can also be infected with this disease, because the vaccine is only 95% effective.
All pregnant women who have had rubella or who have taken the triple viral vaccine while not knowing if they are pregnant should undergo the examinations indicated by the doctor to check for health and fetal development because exposure to the Rubella virus during pregnancy can lead to serious consequences for the baby. Know what these consequences are.
How to treat rubella
The rubella treatment consists of controlling the symptoms of the disease with Paracetamol to reduce pain and fever, as well as rest and hydration so that the person recovers faster and isolated from contact with other family members. Your clothes and personal belongings must be separated until the fever stops and the rash disappears.
Children born with congenital rubella, because they were infected during pregnancy, should be accompanied by a team of doctors, because there are several complications that may be present. Thus, in addition to the pediatrician, children should be seen by specialists and physiotherapists who can assist in their motor and brain development.
The prevention of rubella can be done through the application of the triple-viral vaccine, which protects against mumps, measles and rubella. This vaccine is part of the national immunization schedule for children, but unvaccinated adults can also take this vaccine, with the exception of pregnant women. Know when rubella vaccine can be dangerous.