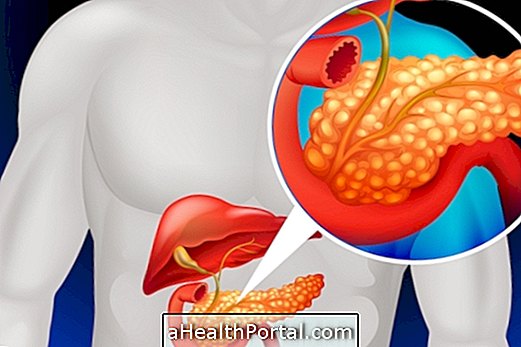
Mitochondrial disease has no cure because it is a genetic alteration where the cells of the affected sites can not survive because the mitochondria, which are responsible for the energy support and survival of the cells, do not function correctly, causing the malfunction of the affected organs, such as brain, eyes or muscles, and can cause blindness or mental retardation, for example.
Depending on each case, the geneticist may prescribe vitamin supplements or specific medications for each mitochondrial dysfunction symptom.
What to do to complete the treatment
There are some simple precautions that complete medical treatment and relieve the symptoms of mitochondrial dysfunction such as:
- Avoid fasting for more than 8 hours : patients with metabolic diseases, such as mitochondrial disease, should avoid staying too long without food, even at night, and it is recommended to eat a snack rich in complex carbohydrates such as bread with peanut butter before of sleeping;
- Do not be exposed to the cold : body temperature control is altered in mitochondrial disease, so it is important to avoid heat loss on very cold days, covering the exposed parts of the body with proper clothing;
- Decrease the use of fats in the diet : the metabolic disease decreases the burning of fats, which can cause the accumulation of body fat. Thus, it is important to reduce the consumption of fatty meals made with oil and butter, as well as yellow cheeses, for example. Here's an example of a low-fat diet: A diet for fat in the liver.
- Reduce the consumption of foods with vitamin C : like orange, strawberry or kiwi, in meals with high level of iron, like red meats, since the excess of iron can cause injuries in the mitochondria. Learn more about these foods in: Foods rich in vitamin C.
- Avoid consumption of ajinomoto : it is usually present in industrialized foods, such as potato chips and soups in powder or canned, for example. Ajinomoto may also be known as monosodium glutamate and it is therefore recommended to read food labels. See other foods with this substance in: Ajinomoto.
However, these precautions do not replace the treatment prescribed by the doctor, and it is necessary to take the medication prescribed by the doctor correctly, which may be antiepileptic medicines, such as Diazepam or Carbamazepine, to avoid the onset of seizures, for example.
Symptoms of mitochondrial disease
The symptoms of mitochondrial disease depend on the affected body sites, the most common being:
Symptoms of mitochondrial disease in the brain
- Delayed development;
- Mental retardation;
- Epilepsy;
- Autism;
- Frequent migraines;
- Insanity.
Symptoms of mitochondrial disease in muscles
- Excessive tiredness;
- Muscle pain;
- Frequent cramps;
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
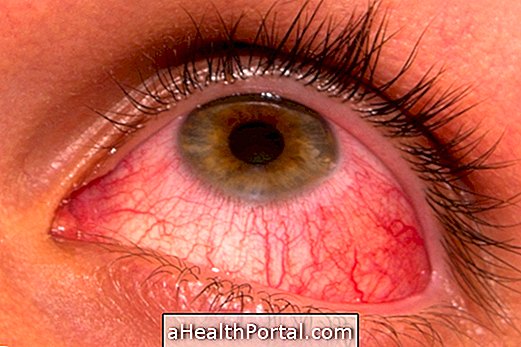
Symptoms of mitochondrial disease in the eyes
- Decreased visual capacity;
- Strabismus;
- Blindness.
In addition, other symptoms such as difficulty gaining weight, vomiting, short stature and serious problems in some organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys and pancreas may also appear.
Symptoms of mitochondrial disease may occur in the adult or soon after birth, as it is usually a genetic disease that passes from the mother to the child during pregnancy, being a maternal inheritance. So when the woman has mitochondrial disease and wishes to get pregnant should do genetic counseling.
Diagnosis of mitochondrial disease
To make the diagnosis of mitochondrial disease, the geneticist must do specific blood tests such as liver enzymes, lactate, pyruvate or amount of amino acids in the plasma, for example, besides doing a muscle biopsy and computed tomography to eliminate other possible health problems which may be triggering the onset of symptoms.