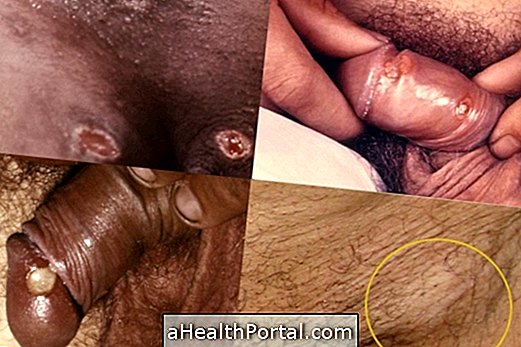
Gonorrhea is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which has as its main characteristic the discharge similar to the pus that exits through the urethra. A person may be contaminated with gonorrhea through:
- Intimate contact without a condom with another contaminated person;
- From mother to child during pregnancy or childbirth;
- Very rarely, by wearing underwear or contaminated objects.
Thus, it is possible to be contaminated during sexual intercourse with the infected person during vaginal, anal or oral contact and so it is important to use a condom in all these situations.

How to know if I have gonorrhea
Some people may not have symptoms in the first few days, although they may already infect others. So if you had sex without a condom last month, be aware of the following signs and symptoms:
In the woman:
- Pain or burning when you urinate;
- Urinary incontinence;
- White-yellow discharge, similar to pus;
- There may be inflammation of the Bartholin glands;
- There may be sore throat and voice impairment (gonococcal pharyngitis, when there is an oral intima relationship);
- There may be obstruction of the anal canal (when there is anal intima relationship).
About 70% of women do not have symptoms.
In the man:
- Pain or burning when you urinate;
- Low fever;
- Yellow discharge, similar to pus, coming from the urethra;
- There may be sore throat and voice impairment (gonococcal pharyngitis, when there is an oral intima relationship);
- There may be obstruction of the anal canal (when there is anal intima relationship).
These symptoms usually appear 10 days after the contamination with the gonococcus but it is also possible that they manifest from 3 to 30 days after the contamination. See more about the symptoms of this disease.
If you suspect that you may be infected you should seek a gynecologist or urologist and perform tests such as the analysis of the secretion that identifies the disease.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for gonorrhea is done with the use of antibiotics usually in a single dose, but the doctor may decide to take the antibiotic for 7, 10 or 14 days depending on the severity of the disease. During treatment it is important that the partner is also treated and that there is no relationship until the complete remission of the disease.