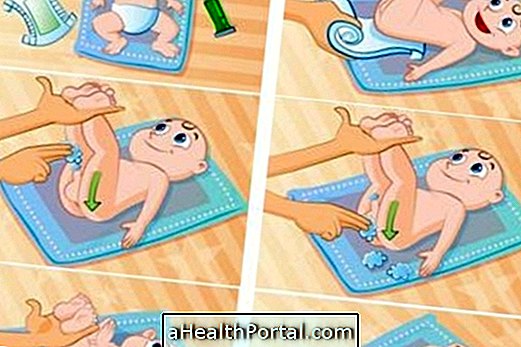
The foot test, also known as neonatal screening or neonatal screening, is a free and mandatory test done on all newborn babies from the 3rd day of life to help diagnose certain diseases, such as phenylketonuria or congenital hypothyroidism.
The test of the foot usually helps to diagnose early congenital diseases that can be treated from the first days after birth to allow to improve the quality of life of the child.
The diseases detected by the basic foot test vary according to the Brazilian State; however, phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism are always investigated.

Diseases detected by the basic foot test
The diseases detected by the basic foot test include:
1. Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is a congenital disease in which the baby's digestive system can not digest phenylalanine, a protein present in foods such as eggs and meat, which, when undigested, can become poisonous to the body, causing neurological impairment in the child's development.
How the treatment is done: eliminate foods with phenylalanine from the child's diet. See: Diet for phenylketonuria.
2. Congenital hypothyroidism
Congenital hypothyroidism is a disease in which the baby's thyroid can not produce normal amounts of hormones, which can impair the baby's growth, as well as cause mental retardation, for example. Learn more about this problem in: Congenital hypothyroidism.
How the treatment is done: Your baby should take hormonal medications to help supplement the levels of missing thyroid hormones, ensuring healthy growth and development.
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic problem that causes changes in the shape of red blood cells, reducing the ability to carry oxygen to the various parts of the body, which can lead to delays in the development of some organs.
How the treatment is done: Depending on the severity of the disease, your baby may need to have blood transfusions. However, treatment is only necessary when infections such as pneumonia or tonsillitis appear. Learn more about this problem in: Sickle cell anemia.
4. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a disease that causes the child to have a hormonal deficiency of some hormones and an exaggeration in the production of others, which can cause excessive growth, precocious puberty or other physical problems.
How the treatment is done: the baby must have hormone replacement throughout his life to compensate for the lack of hormones and stabilize the amount of excess hormones.
5. Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a problem that leads to the production of a large amount of mucus, compromising the respiratory system and also affecting the pancreas. Know other complications and how to treat in: How to know if the baby has cystic fibrosis.
How the treatment is done: It should be done with anti-inflammatory medicines, diet care and respiratory physiotherapy to relieve the symptoms of the disease, especially the difficulty to breathe.
6. Biotinidase deficiency
Biotinidase deficiency is a congenital problem that causes the body's inability to recycle biotin, which is a very important vitamin for ensuring the health of the nervous system. In this way, babies with this problem may present convulsions, lack of motor coordination, delayed development and hair loss.
How the treatment is done: Intake of the vitamin biotin throughout life to compensate for the inability of the body to use this vitamin.
Diseases detected by the enlarged foot test
In addition to the diseases mentioned above, the expanded or expanded foot test can detect other diseases such as:
- Galactosemia : a disease that causes the child to not digest the sugar present in the milk, which can lead to a compromise of the central nervous system;
- Congenital Toxoplasmosis : a disease that can be fatal or lead to blindness, jaundice that is yellowing of the skin, seizures or mental retardation;
- Deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase : facilitates the appearance of anemias, which may vary in intensity;
- Congenital syphilis : a serious disease that can lead to central nervous system involvement;
- Aids : a disease that leads to a serious impairment of the immune system, which has not yet been cured;
- Congenital rubella : causes congenital deformities such as cataracts, deafness, mental retardation and even cardiac malformations;
- Congenital herpes : a rare disease that can cause localized lesions on the skin, mucous membranes and eyes, or disseminated, seriously affecting the central nervous system;
- Congenital cytomegalovirus disease : can generate cerebral calcifications and mental and motor retardation;
- Congenital Chagas disease : an infectious disease that can cause mental retardation, psychomotor and eye changes.
The diseases detected by the plus foot test and the master foot test are part of this list, however they may have these names depending on the laboratory and the number of diseases to be detected.
Generally, the test of the enlarged foot is only carried out if there is suspicion of contamination of the baby, if the mother or father are carriers of any of these diseases.
If the foot test detects any of these diseases, the laboratory contacts the baby's family on the phone and the baby should have a new test to confirm the disease or is referred to a specialist medical appointment.
See other tests your baby should do right after birth.