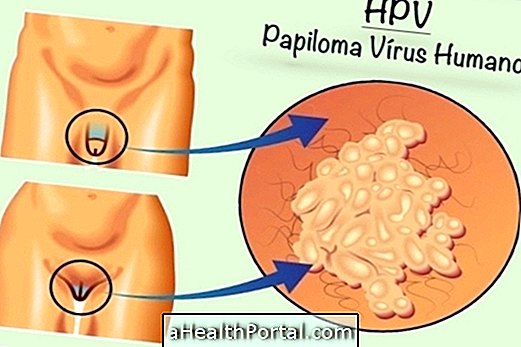
The human papillomavirus is the cause of the sexually transmitted disease popularly known as HPV. It is difficult to cure and manifests itself through symptoms such as warts that arise in the intimate region after intimate contact with an infected individual.
Its treatment is made with the use of drugs and surgeries of cauterization and lasts in average 2 years, although the symptoms disappear a little before.
HPV is also known as: condyloma acuminata, genital warts, cock crest, fig tree, and crested horse.
HPV has a cure
In some people HPV cures itself due to spontaneous remission of the virus. This can happen between 4 weeks and 2 years after virus contamination in people who have a good immune system, who rarely get sick. These people never have any HPV-related symptoms, but they can contaminate others as long as they do not heal.
For people who have found that they have HPV but do not have any symptoms, the doctor can assess whether treatment should be done but despite this it may be useful to invest in home treatments, strengthening the immune system with consumption of foods rich in vitamin C, such as pineapple, acerola and strawberry, for example.
See when HPV cures alone in: When spontaneous remission of HPV occurs.
Usually people with symptoms do not get cured alone of HPV, and treatment is necessary. It is common to have relapses, but whenever the treatment is performed correctly the person gets completely cured. Thus, when the symptoms disappear and with the end of treatment, it can be said that the patient has reached the cure of HPV, which can be confirmed through examinations.
Although treatment is not always enough to cure HPV definitively, treatment is important because HPV infection increases the risk of cancer. To achieve this 'cure' for HPV, it is recommended to use the remedies indicated by the doctor and to use condoms in all relationships.


Symptoms of HPV
The symptoms of HPV are:
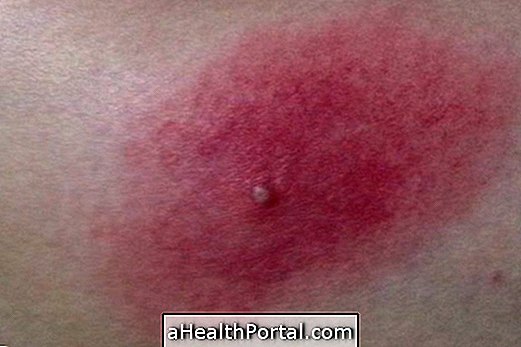
- Several small warts in the male or female intimate region.
- These warts may still be present in the cervix region (not easily visible) and not present in the female outermost region.
Symptoms may be absent despite the presence of the virus. This occurs mainly in men, but it can also happen in women.
The diagnosis of HPV can be made by clinical-visual examination and confirmed by pap smear or biopsy of warts. See all the details of HPV symptoms and photos.
HPV in man
HPV in humans is similar to HPV in women, but it is very common for humans to have no symptoms, although the virus is present in the skin of the genital organ and can be passed on to others through intimate contact. See How to Identify HPV in Men.
Sometimes the virus is naturally eliminated by the body and what can happen is the man to contaminate the partner and this develop symptoms and when he does tests he discovers that he no longer has the virus. So it is not always possible to know who passed the virus on to the other.
The test for identifying HPV in humans is colposcopy and treatment can be done with cryotherapy, laser, solutions and ointments, as well as remedies to strengthen the immune system. The treatment does not interfere with erection and male fertility.
Treatment for HPV
Treatment for HPV can be done with:
- Use of ointments and solutions applied by the doctor in the office;
- Cauterization (laser) surgeries performed from time to time by the physician.
70% and 90% trichloroacetic acid (ATA) and 15% Podofilina in alcoholic solution should be applied by the doctor once a week and the ointment, such as 0.15% Podofilotoxin, should be applied by the person 2 times a day. Treatment for HPV is time consuming and costly, but it is the only way to beat the disease and decrease the risk of cancer in men and women.
See the signs of improvement and worsening in: Treatment for HPV.
What can happen if you do not treat HPV is that the person can transmit the virus to others and can develop cancer.
HPV transmission
The HPV virus is highly contagious and transmission of HPV occurs through intimate condom-free contact with the individual infected with the virus and only 1 contact is likely to become contaminated.
The incubation time of the virus varies from 1 month to 2 years and during this period although there are no symptoms, the individual can already contaminate others because he may already have warts invisible to the naked eye but can pass to the other.
Women can also transmit HPV to the baby during normal delivery.
Here's how to identify early symptoms and what to do to treat HPV by watching the video below:

HPV vaccine
The HPV vaccine is indicated for women and men between 9 and 26 years and serves to lower the risk of cervical cancer, penile and anus. The vaccine is free for all girls between 9 and 13 years of age because it has a 100% efficacy when it is administered before the first intimate contact. From the age of 14, anyone who wants to take the HPV vaccine should buy it at the pharmacy.
Those who have had intimate contact or already have HPV can also take the vaccine because it protects against other types of HPV. After the vaccine is taken, it is still necessary to use condoms in all sexual relations to avoid contamination with other HPV viruses.
Although very effective this vaccine can have side effects. See what they are: HPV vaccine.
Types of HPV viruses
There are more than 100 types of HPV virus, with only 4 of them being cancer-related. Types 16 and 18 cause about 70% of cases of cervical cancer, while types 6 and 11 cause about 90% of genital warts.