Sialolithiasis consists of an inflammation and obstruction of the ducts of salivary glands due to the formation of stones in this region, leading to the appearance of symptoms such as pain, swelling, difficulty swallowing and malaise.
The treatment can be done by massage and stimulation of the production of saliva and in more severe cases, it may be necessary to resort to surgery.
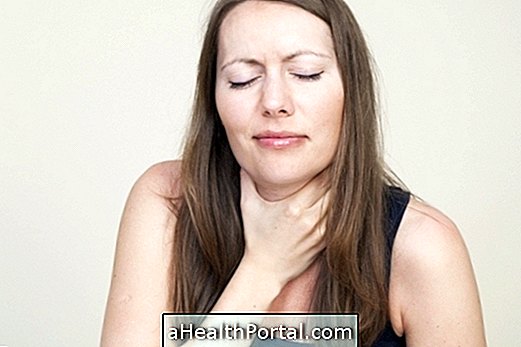
What are the symptoms
The main symptoms caused by sialolithiasis are pain in the face, mouth and neck that may worsen before or during meals, which is when the production of saliva by the salivary glands increases. This saliva is blocked, causing pain and swelling in the mouth, face and neck and difficulty swallowing.
In addition, the mouth may become drier, and bacterial infections can also occur, causing symptoms such as fever, poor taste in the mouth and redness in the area.
Possible causes
Sialolithiasis occurs due to clogging of the ducts of the salivary glands, which is caused by stones that may form due to the crystallization of saliva substances such as calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate, causing saliva to become trapped in the glands and cause swelling.
It is not known exactly what causes the formation of these stones, but is thought to be due to certain medications, such as antihypertensives, antihistamines or anticholinergics, which reduce the amount of saliva produced in the glands, or dehydration that makes the concentrated saliva, or even due to insufficient feeding, which leads to a reduction in saliva production.
In addition, people with gout are more likely to suffer from sialolithiasis, due to the formation of stones by the crystallization of uric acid.
Sialolithiasis occurs more frequently in the salivary ducts connected to the submandibular glands, however, stones may also form in the ducts attached to the parotid glands and very rarely in the sublingual glands.

Diagnosis of sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis can be diagnosed through clinical evaluation and examinations such as computed tomography, ultrasound and sialography.
How is the treatment done?
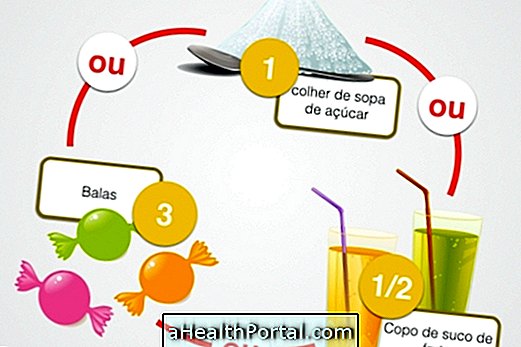
In cases where stone size is small, treatment can be done at home, taking unsweetened sweets and drinking lots of water, in order to stimulate the production of saliva and force the stone out of the duct. You can also apply warmth and gently massage the affected area.
In more severe cases, the doctor may try to remove this stone by pressing on the two sides of the duct so that it leaves, and if this is not possible, surgery may be necessary to remove it. In some cases shock waves may also be used to break the stones into smaller pieces so as to facilitate their passage through the ducts.
In the presence of an infection of the salivary glands, which may occur due to the presence of stagnant saliva, antibiotics may also be needed.