Community pneumonia is a serious lung infection that is caught outside the hospital or within the first 48 hours of hospital stay, causing symptoms such as high fever and chest pain.
According to the Ministry of Health, this disease is difficult to transmit, but the patient should avoid direct contact through kisses or hugs, for example.
Community pneumonia is curable and your treatment can be done by taking antibiotic or antiviral drugs at home.
Community child pneumonia
Pneumonia is one of the major infections in the child, causing symptoms such as high fever, coughing up phlegm, difficulty breathing, poor appetite and excessive tiredness.
Typically, the cause of pneumonia may be difficult to identify, but depending on the child's age, the hypotheses may be reduced, since bacterial pneumonia is more common in infants less than 3 months old and viral pneumonia is more common in children with more than 4 months.
Treatment is initiated with the use of antibiotic medicines, such as Ampicillin or Erythromycin, and can be changed after diagnosis of the cause.
Symptoms of Community Pneumonia
Symptoms include:
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Cough with catarrh;
- Chills;
- Chest pain;
- Weakness and easy fatigue.
When the individual presents these symptoms should seek a pulmonologist doctor in the first 48 to start the appropriate treatment, avoiding serious complications such as generalized infection or coma.
In cases of severe community pneumonia, the symptoms are more severe, including difficulty breathing and fever above 40ºC, and hospital admission is recommended.
Treatment for community-acquired pneumonia
Treatment usually takes about 14 days and is started with the use of antibiotics, such as azithromycin, ceftriaxone, or levofloxacin, because the most common cases are bacterial pneumonia. However, after blood or sputum tests, treatment can be changed to an antiviral drug such as zanovir and rimantadine if pneumonia is caused by viruses.
Symptoms improve around the 3rd day, but if there is an increase in fever or the amount of secretions, it is important to inform the pulmonologist to adjust the treatment after blood and phlegm tests.
Pneumonia can be treated at home; however, in some cases, such as severe pneumonia, in patients with heart failure, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, treatment can be performed at the hospital and supplemented with physiotherapeutic treatment to remove infected secretions and improve breathing.
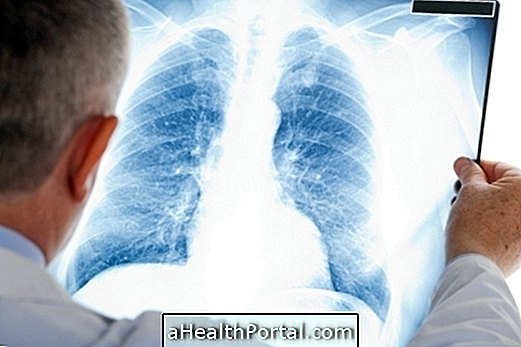
During treatment in patients over 50 years of age, smokers, or who do not show improvement in symptoms, additional tests, such as chest X-rays, may be necessary to observe the evolution of the infection in the lungs.
Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in the elderly
In this case, treatment is done with the use of antibiotic remedy that depend on some factors such as: age of the patient, place where the infection was acquired, possibility of aspiration of pharyngeal secretions or gastric content.
It is very important to maintain good hydration, nutrition and oxygen supply, and treatment in the elderly is mainly done at the hospital.












-o-que--como-identificar-e-o-que-fazer.jpg)