Marrow biopsy is able to study the characteristics of bone marrow cells, so it is often used to help the physician diagnose and monitor the progression of diseases such as lymphoma, myelodysplasias or multiple myeloma, as well as to search for infections or to identify if there are metastases of other types of tumors for this site.
It is possible that this biopsy causes pain at the time of the examination, so it is done with local anesthesia, which helps to ease the discomfort, which can last about 1 to 3 days. Usually, the examination is done by removing a small piece of the bone from the pelvis, which will then be analyzed by the hematologist.
Bone marrow biopsy is indicated by the hematologist, and is usually done to complement the aspirate of the bone marrow, called myelogram, especially when this test can not provide enough information about the bone marrow in a particular disease. To learn more about this bone marrow aspirate, check out Myelogram.
When it is necessary
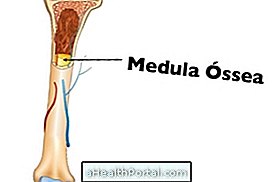
Marrow biopsy is a very important examination because it provides information about the amount and characteristics of the cells that make up the bone marrow. In this way, the test will detect if the marrow is empty or overfilled, if there are deposits of undue substances, such as iron or fibrosis, as well as the presence of any other abnormal cells.
Thus, some of the diseases that can be diagnosed or accompanied by this examination include:
- Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Check out the symptoms and how to identify the lymphoma;
- Myelodysplastic syndrome;
- Chronic myeloproliferative diseases;
- Myelofibrosis;
- Multiple myeloma and other pathologies. Understand what is multiple myeloma and how to treat it;
- Identification of cancer metastases;
- An aplastic anemia and other causes of decreased cellularity of the bone marrow, unclarified;
- Essential thrombocythemia;
- Investigation of causes of infectious processes, such as chronic granulomatous disease.
Marrow biopsy is also used to identify the stage of some types of cancer and to look for organs that have been affected by the disease.
How is it done?
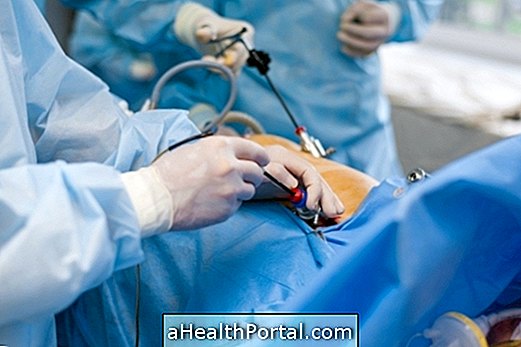
The procedure for spinal cord biopsy can be done at the doctor's office, hospital bed or surgical center, depending on the patient's health status. It is performed using local anesthesia, however, in some cases mild sedation may be necessary, especially in children or patients who can not co-operate with the test.
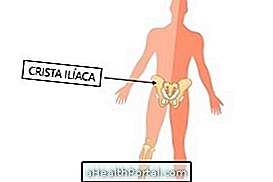
This procedure is usually done in the basin bone, in a place called iliac crest, but in children can be performed on the tibia, a leg bone. Usually, the examination is done shortly after collection of bone marrow aspirate, which can be collected at the same site.
During the examination, the doctor inserts a thick needle, specially developed for this examination, through the skin until it reaches the inner part of the bone, from which a sample of the bone fragment of about 2 cm is removed. then this sample will be placed on slides and laboratory tubes and will be analyzed by the hematologist.
Risks and care after the exam
Marrow biopsy is a safe procedure and rarely brings complications such as bleeding and purple spots on the skin, but it is common for the patient to feel pain during the examination and up to 1 to 3 days later.
The patient may resume normal activities within a few minutes of the examination, preferably at rest on the day of the examination. There is no need to modify the feeding or use of medications, and the dressing at the needle bite site can be removed between 8 and 12 hours after the examination.