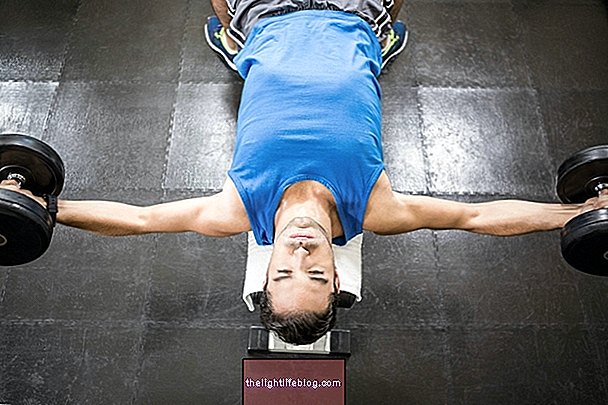
The clinical Pilates consists of an adaptation of several exercises developed by Joseph Pilates by physiotherapists so that they can be performed for people who have never practiced physical activity and also for the rehabilitation of people with spinal problems, to improve posture and various health problems that can be benefited by muscle and joint strengthening.
This training method focuses on breath control, body center of gravity and good posture, which are excellent for increasing concentration and improving motor coordination as well as flexibility of all muscles and tendons, and should preferably be guided by physiotherapists with specific knowledge of Clinical Pilates.

In addition to bringing good physical fitness Clinical Pilates can be used individually and also in group classes of up to 6 people to improve physical fitness in people of all ages.
Main Differences Between Pilates Academy and Pilates Clinic
| Pilates Fitness | Pilates Clinic |
| Certain exercises need physical conditioning to be performed and therefore some may be contraindicated | There are exercises for recovery of injuries but all can be adapted, according to the need of the person |
| Exercises work all over the body | Exercises are very focused on the abdominals and lumbar spine |
| It is characterized by exercises to lose weight, tone and strengthen the whole body | It is characterized by therapeutic exercises that aid in the rehabilitation |
Clinical Pilates exercises can be performed on the floor with the use of elastic, Pilates ball or rug, using the weight of the body itself or with the aid of 9 devices of this method that provide muscle strengthening and increase body awareness.
Both Pilates Fitness and Clinical Pilates can be performed at gyms, Pilates studios or clinics and can be guided by coaches or specialist physiotherapists. However, when there is any illness or symptoms such as back pain or sciatica, it is more advisable to perform Clinical Pilates with the guidance of a physiotherapist and when the goal is to lose weight or shape the body, coach.
Principles of the Pilates Method
The Pilates method is based on 6 principles:
- Concentration;
- Breath;
- Control;
- Centralization;
- Accuracy and
- Fluency of movement.
Thus, those who practice this type of physical activity should be able to perform the exercises perfectly, without overloading the joints, reaching maximum muscle capacity, coordination of movements, correct breathing and maximum attention because to practice the method perfectly is necessary focus attention on the exercise and in all its details.
How is Pilates Method Breathing
The first lesson of Pilates is to learn to breathe properly and to center. This means that the person needs to perform the hardest part of the exercise, ie the contraction, during expiration, when it is releasing air from the lungs. When the body is returning to its initial position it should be inspired, allowing air to enter the lungs. It is not allowed to stay in apnea, that is, without breathing at any time of the exercise.
You can train that lying breathing 10 times in a row as you raise your arm off the ground. So, you should:
- Make the air enter the lungs and when you begin to let the air raise your arm off the ground and
- Lower the arm while it inhales, allowing air to enter.
This breathing requires concentration and is necessary in all Pilates exercises and is most effective because it allows better oxygenation of the brain, the muscle being worked, and all the tissues of the body, requiring that the person focus all his attention on the body. respiration and muscle contraction, which causes him to have more attention to exercise, with a lower risk of injury.
What is centralize
The 'centering' indicated by the creator of the method consists of sucking the pelvic muscles upwards, closer to the rib cage, while maintaining good posture, breathing and performing the movement. And it is precisely because it requires so much coordination that Pilates exercises are so beneficial to the mind and body.
With this type of exercise there is less possibility of muscle compensation and so the risk of injury in classes is much lower.