Laparoscopic surgery is performed with small holes, which greatly reduces the time and pain of recovery in the hospital and at home and is indicated for many surgeries, such as bariatric surgery or removal of the gallbladder and appendix, for example.
Laparoscopy can be an exploratory surgery when it serves as a diagnostic or biopsy examination or is a surgical technique for treating some disease, such as removing a tumor from an organ.
In addition, almost all individuals can undergo laparoscopic surgery for indication of the physician, however, in some cases, already in the operating room and even during laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon may need to perform an open surgery for the treatment to succeed. which implies making a bigger cut and the recovery is slower.


Most common laparoscopic surgeries
Some of the surgeries that can be performed by laparoscopy can be:
- Bariatric surgery;
- Removal of inflamed organs such as gallbladder, spleen or appendix;
- Treatment of abdominal hernias;
- Removal of tumors, such as rectum or colon polyps;
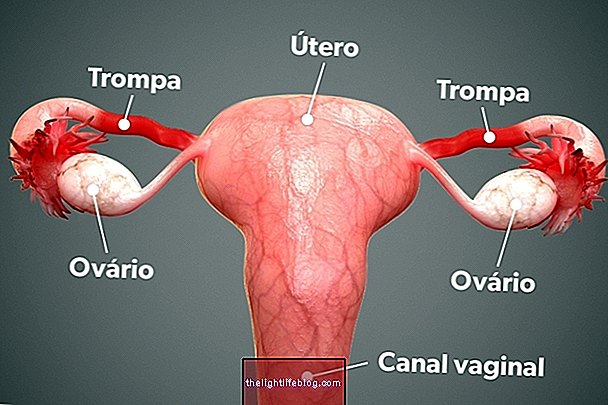
- Gynecological surgery, such as hysterectomy.
In addition, laparoscopy can often be used to determine the cause of pelvic pain or infertility and is an excellent way both for the diagnosis and for the treatment of endometriosis, for example.
How Laparoscopy Works
Depending on the purpose of the surgery, the doctor will perform 3 to 6 holes in the region, where a micro camera with a light source will enter to see the inside of the body and the instruments needed to cut and remove the organ or some affected part, leaving scars very small with about 1.5 cm.


The doctor will be able to observe the internal area through a small camera that enters the body and will generate the image in the computer, being a technique known as videolaparoscopy. However, this surgery requires the use of general anesthesia and therefore it is usually necessary to be hospitalized for at least one day in the hospital.
Patient recovery is much faster than conventional surgery, where a large cut is necessary, so the chances of complication are lower and the risk of pain and infection is lower.