Elbow pain is a very common symptom in people who practice bodybuilding, especially after doing a workout strengthening the triceps, but can also affect people or engage in intense sports with arms such as crossfit, tennis or golf, for example.
Usually, the elbow pain does not indicate a serious problem, but can cause great discomfort because the elbow is a joint used in almost all movements of the arm and hand.
The elbow pain is healing, but in most cases it is necessary to consult an orthopedist or a general practitioner to make the appropriate treatment, which may include medicine and physical therapy.
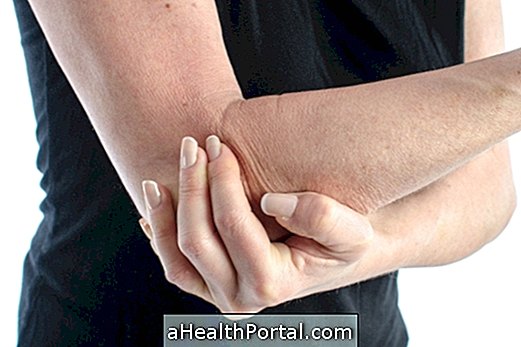
Main Causes of Elbow Pain
The main causes of elbow pain are tendinitis, bursitis or arthritis, however, other more rare causes, such as arm fracture or ulnar nerve compression, can also lead to pain in the area. Learn more about each:
1. Epicondylitis
It is inflammation of the tendons of the elbow, which can be lateral or medial. When it affects only the inner part of the elbow is called the golfer's elbow and when it affects the side of the elbow is called the tennis elbow. Epicondylitis causes pain when making arm movements, even using a mouse on the computer, and hypersensitivity when touching the elbow. The pain gets worse when the person tries to stretch the arm and always gets worse when trying to flex the arm. It usually arises after playing sports or after bodybuilding, such as triceps-forehead exercise, for example.
- What to do: To relieve the pain in the elbow, you should rest, put ice packs in the area, take anesthetic medicines, such as Paracetamol, and do physiotherapy.
Learn more about treating the main cause of elbow pain in: Lateral epicondylitis.
2. Bursitis in the elbow
It is an inflammation of the tissue that serves as a "damper" of the joint, pain affects the back of the elbow arising when the elbow is often placed on hard surfaces, such as tables, for example, and therefore is very common in students, people with rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
- What to do: To cure elbow pain you should rest, apply cold compresses, take anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen, prescribed by your doctor or do physical therapy.
3. Arthritis in the elbow
It is the wear and inflammation of the elbow joint that generates pain and swelling in the region, being more common elderly patients.
What to do: Elbow pain treatment should be done by an orthopedist or general practitioner and usually includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as naproxen and physical therapy.
4. Arm fracture
It can occur after strong impacts, such as accidents, falls or bumps that break a region of the bone near the elbow, and may also affect the arm or forearm.
- What to do: The elbow pain usually does not reduce with the use of pain medication or the placement of compresses, so if you suspect you should go to the emergency room to be immobilized.
5. Ulnar nerve compression
This compression is most common after orthopedic surgeries and generates symptoms such as tingling of the arm, the ring finger or pinky, lack of muscle strength and in the movements of folding or opening these fingers.
- What to do: Should be treated by an orthopedist through physical therapy or surgery to reposition the nerve, depending on the severity of the case.
Plural synovium
The synovial plica is a normal fold that exists inside the capsule that forms the elbow joint, when it increases in thickness it can cause pain in the region behind the elbow, can be heard cracking or bend or stretch the arm, pain arises when folding and Stretch the arm with your hand down. Magnetic resonance imaging is the only examination that can show the increase of the plica, which should not be greater than 3 mm.
- What to do: In addition to passing ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect, physical therapy is recommended.
When to seek medical advice
It is advised to seek a doctor when the pain in the elbow arises suddenly with chest tightness or when:
- Pain comes with fever;
- Swelling and pain increase constantly;
- Pain arises even when the arm is not being used;
- The pain does not pass even taking analgesic and getting to rest.
In these cases it is recommended to consult an orthopaedist to ask for tests and indicate the cause, as well as the best treatment for the case.