The disc herniation is characterized by the bulging of the intervertebral disc, which can lead to symptoms such as back pain and burning sensation or numbness. It is most common in the cervical spine and lumbar spine, and can be treated with medication, physical therapy or surgery, and depending on its severity, can be completely cured.
The herniated disc can be classified according to the region of the spine that it affects and, therefore, it can be:
- Cervical disc herniation: affects the neck region;
- Thoracic disc herniation: affects the middle region of the back;
- Lumbar disc herniation: affects the lower back.
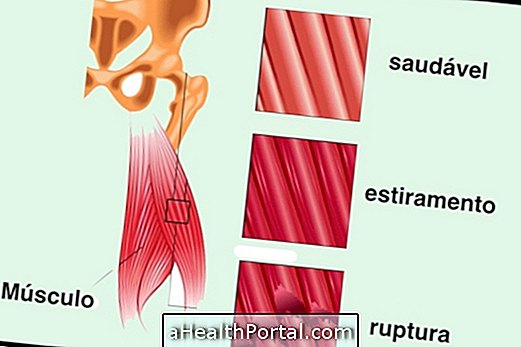
The vertebral disc is a fibrocartilage structure that serves to avoid direct contact between one vertebra and another, and cushion the impact generated by the jumps, for example. Thus, a disc injury, or discopathy, as this condition is also known, impairs the function of the vertebral disc itself and also presses other important structures of the spine, such as the nerve root or the spinal cord.

Types of Herniated Disc
The onset of a disc injury can happen when the person does not have a good posture, does weight lifting without bending the knees and does not eat about 2 liters of water a day. In this case, although it has not formed a hernia, the disc is already damaged, has less thickness, but still retains its original format: oval. If the person does not improve his posture and his life habits in a few years, he will probably develop a herniated disc.
The hernia occurs when the vertebral disc loses its original shape, ceasing to be oval, forming a bulging, which is a kind of 'drop', which can press the root of the sciatic nerve, for example. Thus, the 3 types of herniated disc that exist are:
- Protusa disc herniation: it is the most common type, when the disc nucleus remains intact, but there is already loss of the oval form;
- Extraneous disc herniation: when the disc nucleus is deformed, forming a 'drop';
- Abducted disc herniation: when the core is badly damaged and can even divide into two parts.

A person may have more than one herniated disc and it may increase in severity over time. Usually when the person has only dehydration of the disc, she has no symptoms and only finds out if she does an MRI for any other reason. Symptoms commonly arise when the hernia has already worsened and is in the protrusion stage.
The hernia should still be classified according to its exact location, and can be postero or posterolateral. A posterolateral disc hernia can press the nerve causing a tingling sensation, weakness or loss of sensation in an arm or leg, but when there is a herniated disc posteriorly, the pressured region is the spinal cord and therefore the person can present these symptoms on both arms or both legs, for example.
Symptoms of disc herniation
The main symptom of a herniated disc is the intense pain where it is located, but it can also generate the following symptoms:
| Cervical disc herniation | Lumbar disc herniation |
| Pain in the neck or neck | Pain in lower back |
| Difficulty in moving the neck or raising the arms | Difficulty moving, lowering, getting up or turning in bed, for example |
| There may be a feeling of weakness, numbness or tingling in one of the arms, elbow, hand or fingers | Sensation of numbness in the buttocks, and / or legs, in the back, front or inner of one of the legs |
| --- | Burning sensation in the path of the sciatic nerve that goes from the spine to the feet |
The pain of a herniated disc usually worsens with movements and may be aggravated by coughing, laughter, and may worsen when the subject pees or withdraws, may appear suddenly or worsen over time.
How the Diagnosis is done

The diagnosis of the herniated disc can be made through observation of the symptoms and the physical examination, but it can also be confirmed by examinations, such as CT or MRI, to evaluate the disc, its thickness, the exact location of the hernia and what type of hernia the person has.
The x-ray examination does not clearly show the hernia but may be sufficient to show the alignment of the spine and the integrity or destruction of the vertebrae and so, sometimes the doctor initially requests the X-ray and with the result of the X-ray, requests the resonance or tomography to assess severity.
By confirming that there is one or more disc hernias, your doctor may indicate the treatment that can be done with physical therapy, Pilates, RPG, osteopathy, or surgery. Usually surgery is the last treatment option, being reserved for cases where the person does not show improvement of the symptoms with the other forms of treatment, for a period superior to 6 months.
What Causes Herniated Disc
The main cause of herniated disc is poor posture in the day to day, and the fact that the person is not careful when lifting and carrying very heavy objects. So it is common for people who work as servants, painters, maids, drivers and masons to develop disc herniation or disc herniation around the age of 40.
About 10 years before discovering a herniated disc it is common that the person has already presented symptoms like back pain that does not cease quickly. This is one of the first warning signs that the body emits, but is usually ignored, until the hernia in the spine arises.
Some factors that favor the installation of the hernia are aging, excess weight and inadequate physical effort, and therefore, for the success of the treatment it is important to eliminate all these factors.
Treatments for herniated disc
When the treatment is performed correctly, the symptoms may disappear within 1 to 3 months, but each individual responds in a manner to the treatment and therefore in some cases this period may be greater. For the success of the treatment it is important to know the exact location of the hernia and its type. The most common type, which is the disc protrusion, can be treated with:
- Use of analgesics and anti-inflammatories prescribed by the physician;
- Physiotherapy sessions with equipment, stretches and individualized exercises;
- Osteopathy consisting of popping the spine and realigning all bones and joints;
- Exercises such as RPG, hydrotherapy or Pilates guided by a physiotherapist.
During treatment it is recommended that the person move away from the activities that have caused the hernia, does not make efforts and does not practice any type of physical activity.
Check out these and other tips in the following video:

Herniated disc surgery is indicated when the person has a herniated disc that has been extruded or sequestered, and clinical and physiotherapeutic treatment has not been enough to reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life of the individual.
Herniated disc in pregnancy
A woman who has already diagnosed herniated disc before becoming pregnant should know that during gestation the herniated disc can worsen, causing severe back pain that can press the nerve roots, such as the sciatic nerve. When the sciatic nerve is affected the woman feels pain in the back, the buttock or behind the thigh.
This happens because during pregnancy progesterone leads to increased loosening of all the ligaments in the body, and since the spine also has ligaments, they become more elastic and eventually allowing the vertebrae to drain a little, which can aggravate or cause a herniated disc.
During pregnancy, no medicines other than acetaminophen should be taken, so if the woman has back or gluteal pain, she should lie down with her legs resting on a pillow or pillow, for example. Putting a warm compress on the pain site can also relieve this discomfort. Know the risks to the baby, how the delivery is, and the treatment options for herniated disc in pregnancy.







.jpg)