The allergic reaction to the sun, scientifically called "summer lucite", is a type of allergy caused by UVA rays. It usually affects women between the ages of 15 and 35, who have fair skin, are elderly, or use photosensitive substances for the treatment of acne or skin blemishes, for example.
Individuals predisposed to have other types of allergy are also more likely to have reactions to the sun.
Symptoms of allergic reaction to the sun
Symptoms of allergic reaction to the sun:
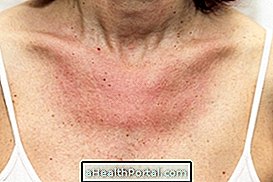
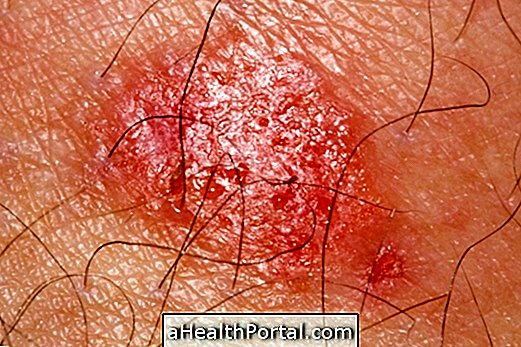
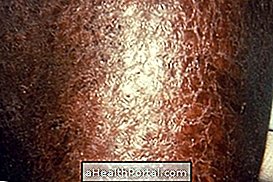
- small red balls on the skin exposed to the sun,
- intense itching at the site of these balls.
The most affected sites are the chest, arms and legs and these symptoms can appear up to 12 hours after sun exposure. Know all the symptoms this allergy can cause in How to Identify Sun Allergy.
Sun allergy usually persists for several years, but may disappear from one moment to the next, although when installed, water and sand may aggravate its symptoms.
Causes of allergic reaction to the sun
The causes of allergic reaction to the sun may be:
- genetic predisposition,
- existence of other allergies,
- allergy to exposure to UVA rays,
- ingestion of drugs.
The use of medications such as antibiotics, antifungal, antihistamines, analgesics, anesthetics and even cosmetic preservatives can increase sensitivity to the sun's rays, favoring allergic reactions also in the sun.
Treatment for allergic reaction to the sun
The treatment for allergic reaction to the sun is non-specific, ie it consists of washing the region with cold water and keeping it protected from the sun, with the use of clothing and sunscreen.
Pictures of allergic reaction to the sun