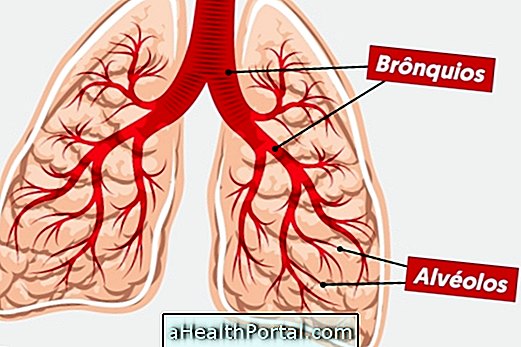
Bronchopneumonia is a type of lung infection that can be caused by viruses, fungi, or bacteria. Although it is a type of pneumonia, in addition to affecting the alveoli of the lung, bronchopneumonia also affects the bronchi, which are the largest routes through which air enters the lungs.
Due to the inflammation of the bronchi, the air can not enter easily into the lungs, so it is very common to develop symptoms like intense shortness of breath, pale skin, bluish lips and very easy tiredness.
Generally, treatment can be done at home and is started with the use of antibiotics, since bacteria are primarily responsible for the infection, however, it may be necessary to change the treatment if it is not working. Thus, you should always consult a pulmonologist to make the most appropriate treatment and evaluate over time.
Main symptoms
To identify if it is a bronchopneumonia, one must be alert to the appearance of symptoms such as:
- Fever above 38 ° C;
- Difficulty breathing and shortness of breath;
- Tiredness and muscle weakness;
- Chills;
- Cough with catarrh;
- Increased heart rate;
- Blue lips and fingertips.
Symptoms in baby and child
In the baby and the child, the symptoms may be slightly different, and usually include:
- Fever;
- Breathing noisy and fast;
- Catarrh;
- Tiredness and drowsiness;
- Easy irritability;
- Difficulty sleeping;
- Lack of appetite.
Bronchopneumonia in the baby is very common, since its immune system is still underdeveloped, which facilitates the development of bacteria and other microorganisms that can cause this type of infections. As soon as the first symptoms appear, it is important to consult your pediatrician promptly to prevent the worsening of the disease.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of bronchopneumonia can be made by a general practitioner, a pulmonologist or even a pediatrician in the case of children. Generally, to get the diagnosis, in addition to evaluating the symptoms, the doctor also listens to breathing with the stethoscope and can ask for other exams such as chest x-rays, blood tests, CT or bronchoscopy, for example.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of bronchopneumonia in most cases can be done at home by taking antibiotic medicines such as ceftriaxone and azithromycin, which fight the major microorganisms responsible for causing the disease. In addition, the general practitioner or pulmonologist may also recommend the use of remedies to alleviate and cough cough or a liquid diet to prevent dehydration.
Generally, the treatment lasts on average 14 days and during this time it is recommended to take other care as:
- Rest and avoid making efforts;
- Avoid sudden temperature changes for a correct recovery;
- Drink at least 2 liters of water;
- Make regular nebulizations with saline;
- Avoid smoking or smoking.
In addition, to prevent transmission of the disease should also cover the mouth to cough, wash hands regularly and should avoid going to public places and closed.
In more severe cases, bronchopneumonia can lead to hospitalization, where it may be necessary to receive oxygen, make antibiotic injections and perform Respiratory Physiotherapy, which helps to release the respiratory tract.
When the first symptoms of bronchopneumonia occur, it is important to go to the general practitioner or pulmonologist to perform a chest X-ray and pulmonary auscultation, so that the disease can be diagnosed and its treatment can begin.
Possible Causes and How to Avoid
Bronchopneumonia is caused by various types of fungi, viruses and bacteria that can be transported through the air or through objects and hands. Therefore, some ways to avoid catching the infection include:
- Do the flu vaccination ;
- Wash your hands regularly, especially before eating or touching your face;
- Avoid smoking or frequenting places with heavy smoke;
These measures are especially important in the case of children and the elderly, as well as people with immune systems weakened by diseases such as asthma, diabetes, lupus or HIV.