Changes in the gut are common causes of pain in the belly, which can be caused by both mild causes and do not generate much discomfort, but can also have serious causes and that, if not quickly treated, can put one's life at risk.
Some of the more common causes include constipation, infections, food intolerance, inflammation or even tumors that can cause pain and other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in stool. To identify what may be the pain in the belly, and confirm whether or not it is due to a change in the gut, it is very important to seek care with the doctor, who can make the clinical evaluations and ask for tests that confirm the cause.

Although only medical evaluation can accurately identify what is involved in bowel pain, we summarize some of the main causes, including:
1. Constipation
Also known as constipation or constipation, constipation arises when there are fewer than 3 bowel movements per week, causing dry, hardened stools that are more difficult to eliminate, and a sensation of incomplete bowel emptying, bloating, and abdominal discomfort.
Constipation is very common, and it is more common in people who do not have a habit of routinely using the toilet, holding the urge to defecate, in addition to poor diet in fiber and water, use of certain medicines, such as antidepressants, anti inflammatory, corticoid or psychotropic, and diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, Parkinson's or other neurological diseases, for example.
- What to do : In addition to changes in eating habits, increasing the amount of fiber and water in the diet, it is recommended to seek medical attention to guide the need for laxatives, or treatment for the cause that caused this symptom. Learn more about what to do to fight constipation.
2. Diarrhea
It occurs when there are 4 or more bowel movements per day, with a change in consistency and stool content. The most common cause is gastroenteritis, caused by viral or bacterial infections, which causes abdominal pain due to increased peristalsis and contractions in the intestine, in addition to nausea, vomiting and, in some cases, fever.
Other causes of diarrhea and abdominal pain also include intestinal worms, diseases that cause changes in food absorption, such as in celiac disease, food intolerance, use of medicines or irritable bowel, for example. Learn more about the causes of diarrhea.
- What to do : The treatment of diarrhea depends on the cause, and is doctor-directed, and may include antibiotics to treat infections, anti-spasms to reduce colic, hydration, and care of food.
Irritable bowel syndrome
Also known as irritable bowel syndrome, it is a functional bowel disorder causing pictures of abdominal pain that improve after defecation, as well as changes in the frequency, consistency and appearance of the stool, alternating between periods of diarrhea and constipation. Although the exact cause of this syndrome is not understood, it is known to be worsened during periods of stress and anxiety.
- What to do : In case of suspected irritable bowel syndrome, it is necessary to seek medical attention from the gastroenterologist, who can perform the clinical evaluation and request tests that may exclude other causes and confirm the disease. Some medications such as analgesics, antispasmodics, constipants or laxatives may be helpful in relieving the symptoms. Learn more about treatment options for this syndrome.
4. Food intolerance
The intolerance to certain foods, including the most common ones like lactose, gluten, yeast, alcohol or fructose, for example, are important causes of symptoms like belly pain, diarrhea, discomfort and abdominal bloating.
Generally, intolerance is brought about by the lack of the enzyme responsible for the digestion of food, the symptoms usually arise or worsen always after eating the foods responsible.
- What to do : If food intolerance is suspected, follow up with the gastroenterologist in conjunction with the nutritionist is indicated. Generally, it is advisable to avoid food, however, in some cases it is possible to replace the missing enzyme. Check out more about how to know if it is food intolerance and what to do.

5. Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is characterized by Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, and although the exact causes of these diseases are not known, they are known to be related to autoimmune and genetic issues.
In inflammatory bowel disease, inflammation affects the intestinal wall, and can also occur anywhere in the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, rectal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness, nausea, vomiting, bleeding, fever and anemia.
- What to do : Follow up with the gastroenterologist, who may indicate medications that help decrease inflammation, such as sulfasalazine. In some cases it may also be necessary to perform surgeries. Learn more about these diseases in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
6. Intestinal obstruction
Bowel obstruction is a medical emergency, and can occur due to situations such as volvulus, which is twisting of the intestine, a strangulated hernia or tumors in the intestine, for example.
An obstruction can occur in both the small and large intestines, and causes accumulation of gas, feces and fluids, triggering an intense inflammation in the bowel, severe abdominal cramps, bloating, loss of appetite and vomiting.
- What to do : In the presence of signs and symptoms that indicate bowel obstruction, it is necessary to go to the emergency room, where the doctor will make tests, such as a radiograph of the abdomen, in addition to the clinical evaluation, to confirm or not confirm this change.
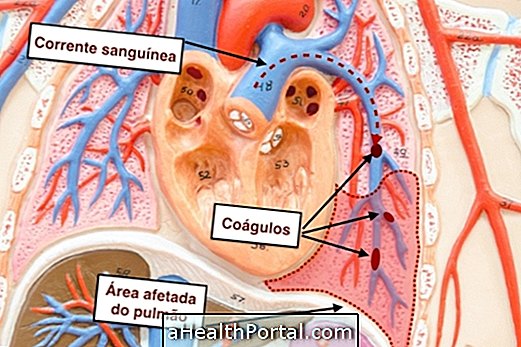
7. Intestinal infarction
Intestinal infarction arises when there is an obstruction of blood flow to the blood vessels that irrigate these organs. It causes severe abdominal pain, vomiting and fever, and should be treated quickly to reduce the health risks of the affected person.
Intestinal ischemia is also caused by obstruction of blood flow, and can also cause pain, and can be acute or chronic, with a more painful picture of pain that arises mainly after eating.
- What to do : After detecting this change, the doctor may indicate that surgery is performed to remove necrotic parts of the intestine or to assist in clearing the blood vessel. Understand better in: Infarct of the intestine.

8. Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is the inflammation and infection of the diverticula, which are small folds or sacs that arise in the walls of the large intestine, and causes pain in the abdomen, changes in the bowel, vomiting, fever and chills.
- What to do : the treatment is done with antibiotics, analgesics, hydration and changes in diet. Only in some cases where complications arise, surgery may be indicated. Learn more about what is and how to treat diverticulitis.
9. Appendicitis
It is an inflammation of the appendix, which is a small organ located on the right side of the abdomen, which has direct attachment to the intestine. This inflammation is severe, causes severe pain in the right and lower abdomen, in addition to vomiting, fever and feeling sick.
- What to do : the main way to treat appendicitis is by performing surgery, and antibiotics and hydration are also indicated. Learn more about what appendicitis is and how to identify it.
10. Intestinal tumor
Cancer in the gut is among the causes of abdominal pain, although it is less common. Intestinal cancer is suspected when, in addition to changes in bowel rhythm, there is weight loss, abdominal pain or bleeding in the stool, for example.
- What to do : After performing tests that identify the tumor, the treatment is guided by the oncologist, and includes chemotherapy, radiation and / or surgery sessions. See more details on treating bowel cancer.