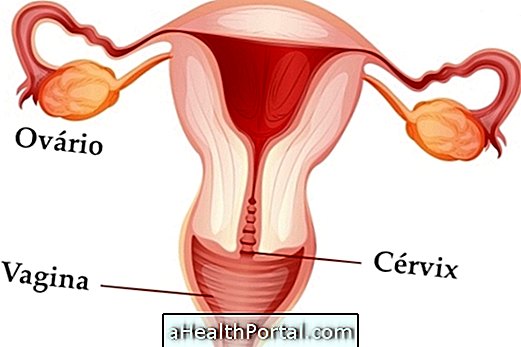
The menstrual cycle usually lasts about 28 days and is divided into 3 phases, according to the hormonal changes that occur in the woman's body during the month. Menstruation represents the fertile years of a woman's life, which begin in adolescence and last through the menopause.
It is normal for the cycle duration to vary between 25 and 35 days, but cycles with shorter or longer intervals than these may represent health problems such as polycystic ovary, so if this happens it is advisable to consult a gynecologist.
Menstrual Cycle Calculator
Find out what your menstrual cycle is by entering the following data:

When the menstrual cycle is irregular, it is more difficult to know the day of ovulation and it may be more difficult to get pregnant, because the fertile period can not be accurately calculated. Here's how to calculate the fertile period of irregular cycles.
Stages of the normal menstrual cycle

The normal menstrual cycle lasts, on average, 28 days, beginning on the first day of menstruation and ending when the next month's menstruation begins. Each cycle is divided into 3 phases:
1. Follicular phase
This is the first phase of the cycle, which starts on the first day of menstruation and lasts 5 to 12 days. At this stage the brain increases the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which causes the ovaries to mature their eggs.
With this maturation, the ovary also begins to release higher amounts of estrogen, which is another hormone, responsible for making the lining of the uterus ready for a possible pregnancy.
2. Ovulatory phase
At this stage, estrogen levels continue to increase and lead the body to produce the luteinizing hormone (LH), which is responsible for selecting the more mature ovum and getting it out of the ovary, which is when ovulation usually occurs around ovulation of the 14th day of the cycle.
Once released, the egg travels through the tubes until it reaches the uterus. Normally, the ovum survives for 24 hours outside the ovary and therefore, if it comes in contact with sperm, it can be fertilized. Since sperm can last up to 5 days inside the woman's body, it is possible that if the woman has had intercourse up to 5 days before ovulation, she may become pregnant.
3. Luteal phase
This phase occurs on average in the last 12 days of the cycle and during these days the follicle, left by the ovule inside the ovary, begins to produce progesterone in greater quantity, to continue preparing the lining of the uterus in the case of a possible pregnancy. In addition, there is also an increase in estrogen production and therefore some women may have breast tenderness, mood swings and even bloating.
When fertilization does not occur, the follicle shrinks inside the ovary, so the levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease until the lining of the uterus is eliminated, initiating menstruation and the next menstrual cycle.
If fertilization does occur, the egg is stuck to the walls of the uterus and the body begins to produce hCG, a hormone that keeps the follicle producing estrogen and progesterone at high levels to keep the lining of the uterus until placental formation.
Signs indicating fertile period
Signs that indicate fertile time are clear discharge similar to egg white, increased breast tenderness and mild pain in the uterus, similar to a mild and transient colic.
In addition to these signs, it is also possible to identify ovulation through the ovulation pharmacy test, such as Confirme and Bioeasy. Here's how to use these tests to see if you're in the breeding season.
What leaves the irregular menstrual cycle
The irregular menstrual cycle is one in which it is not known when menstruation will come. The most common causes of irregular cycling are:
- Early fertile life in adolescence, up to 2 years after first menstruation;
- Post-pregnancy period;
- Premenopause due to intense hormonal changes;
- Eating disorders that cause excess weight loss, such as anorexia nervosa;
- Excessive physical activity, especially in female athletes;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Polycystic ovary;
- Change of contraceptive;
- Stress or emotional disturbances;
- Presence of inflammation, polyps or tumors in the female reproductive tract.
In the presence of an irregular menstrual cycle or when the menstrual cycle does not occur for more than 3 months, one should seek out the gynecologist to investigate the cause of the problem. See 10 Myths and Truths about Menstruation.