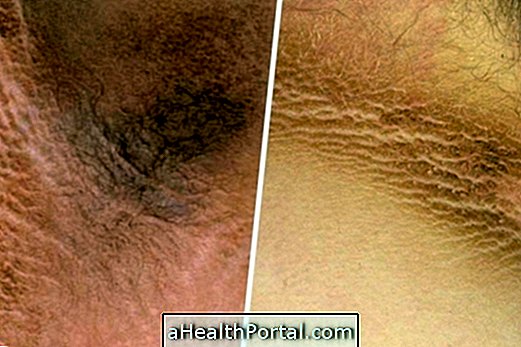
Stasis dermatitis, or stasis eczema, corresponds to a chronic inflammation of the skin that occurs in the lower part of the legs, especially in the ankles, due to the difficulty of the blood returning to the heart, accumulating in the region. This chronic disease is characterized by a change in the color of the skin, which is darkened due to desquamation, heat and edema.
The treatment is done according to the guidance of the dermatologist and should be done as soon as possible to avoid the emergence of complications such as ulcers, for example.


Main cause
The main cause of stasis dermatitis is venous insufficiency, that is, when blood can not return to the heart, accumulating in the legs. Thus, this type of dermatitis occurs more frequently in women with varicose veins and swelling in the legs.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of stasis dermatitis is aimed at resolving venous insufficiency, that is, allowing the circulation to be normalized, thus reducing the accumulation of blood in the lower legs.
The dermatologist usually recommends using elastic compression stockings and advise the person not to sit or stand for long. In addition, wet compresses, ointments for the site of inflammation or oral antibiotics may be indicated according to medical advice. It is also important to take care of how to protect the lesions to avoid infections and, when possible, raise your legs to prevent blood from accumulating.
It is not recommended to pass creams, ointments or use antibiotics that have not been recommended by the doctor, as it can worsen inflammation, leading to complications such as contact dermatitis, infectious cellulitis, and the appearance of varicose ulcers, which are difficult to heal wounds located at the ankle. due to poor circulation. When ulcers are very aggressive, it may be recommended to perform skin grafts to regenerate the affected tissue. Understand varicose ulcers and how treatment is done.
Symptoms of stasis dermatitis
The symptoms usually associated with stasis dermatitis are:
- Red and hot skin;
- Desquamation;
- Darkening of the skin;
- Lack of blood circulation in the ankles;
- Wounds at the site of inflammation;
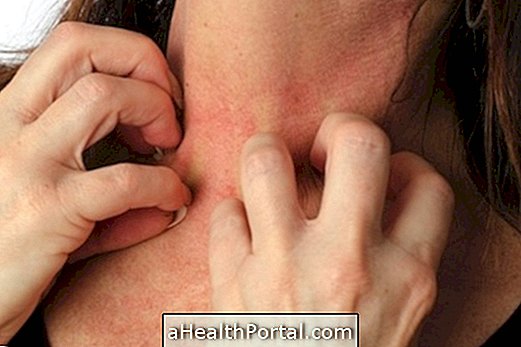
- Itching;
- Swelling;
- Higher chance of bacterial infections.
When the symptoms appear, it is important to consult a dermatologist for the diagnosis and appropriate treatment can be initiated.
Diagnosis is usually made by observing the symptoms and characteristics of the skin, but laboratory tests may also be required to evaluate blood flow and imaging tests such as ultrasonography.