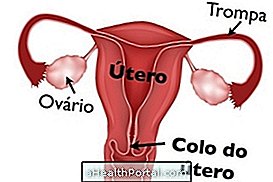
The colpitis corresponds to inflammation of the vagina and cervix caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa and leads to the appearance of white and milky vaginal discharge. This inflammation is more common in women who have frequent intimate contact and who do not use condoms during intercourse, especially.
The diagnosis of colpitis is made by the gynecologist from the analysis of the symptoms described by the woman, observation of the intimate region and some tests to confirm the disease. From the identification of the microorganism causing the colpitis, the doctor can indicate the best treatment.
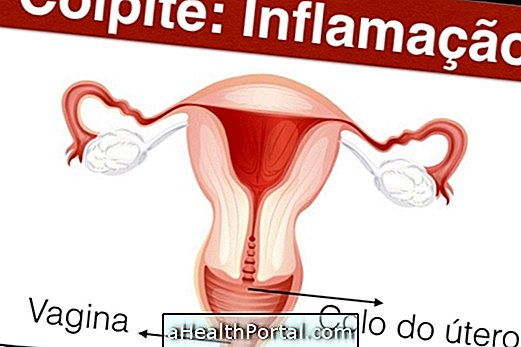
Types of colpite
According to the cause, the colpite can be classified in:
- Bacterial Colitis: This type of colitis is caused by bacteria, especially Gardnerella sp . Inflammation caused by infection by this genus of bacteria leads to the onset of vaginal discharge of unpleasant odor and pain during intimate contact. Learn how to identify Gardnerella sp .
- Fungal colitis: Fungal colitis is caused mainly by fungi of the genus Candida, which is usually present in the woman's vagina, but in the presence of favorable temperature and humidity, can proliferate and cause infection. See how treatment for genital candidiasis is done.
- Colposite by protozoa: The main protozoan responsible for colitis in women is Trichomonas vaginalis, which causes burning sensation, burning and a strong urge to urinate. Learn to identify the symptoms of trichomoniasis.
In order to know which microorganism is responsible for the collection, it is necessary for the gynecologist to request a microbiological examination that must be done through the collection of vaginal secretions, which is performed in the laboratory. From the result of the examination, the doctor can establish the treatment according to the cause.
Colitis can also be classified according to the signs and symptoms presented in:
- Diffuse colpitis, which is characterized by the presence of small red spots on the vaginal mucosa and cervix;
- Focal colpitis, in which round red spots may be seen on the vaginal mucosa;
- Acute colpitis, which is characterized by swelling of the vaginal mucosa beyond the presence of red dots;
- Chronic colpitis, in which white and red dots are observed in the vagina.
From the observation of the signs during the gynecological exam, the doctor can indicate the severity of the inflammation, as well as evaluate the risk of complications such as endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease, for example.
Main symptoms
Vaginal inflammation is characterized primarily by the presence of homogeneous, milk-like vaginal discharge, which may also be bullous. Some women may also feel unpleasant odor, usually similar to fish, and it worsens after intimate contact. In addition, small red or white speckles may be observed in the vaginal mucosa and cervix, as well as swelling of the uterus. Learn more about colitis symptoms.
The diagnosis of colpitis is done by the gynecologist through examinations such as colposcopy, the Schiller's test and the pap smear, for example, however the pap smear is not very specific for the diagnosis of colpitis and does not show very well the signs of vaginal inflammation . Meet the Schiller test.
How is the treatment?
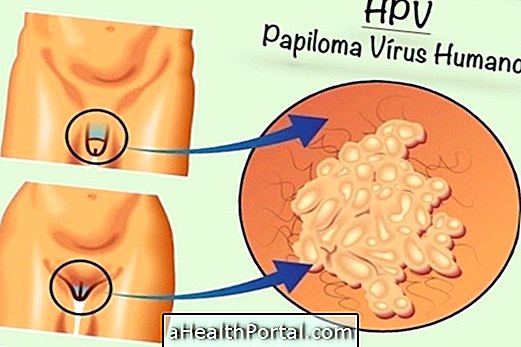
The treatment of colpitis is done with the use of medications that must be administered orally or applied directly to the intimate region. Although not a serious condition, vaginal inflammation should be treated as soon as possible, to avoid worsening of the lesion, since it facilitates the occurrence of other diseases such as HPV and AIDS, for example.
During the treatment it is recommended that the woman does not have intercourse, even with a condom, because the friction of the penis in the vagina can be uncomfortable. See how treatment is done for colitis.