Physiological saline, also known as 0.9% sodium chloride, is a sterile saline solution used to make intravenous infusions in cases of decreased fluid or salt in the body, cleaning of the eyes, nose, burns and wounds or to make nebulizations.
This product can be purchased in conventional pharmacies without prescription in the form of plastic bottles, whose price may vary according to the amount of liquid in the package.
Saline can be used in several situations:
1. Dehydration

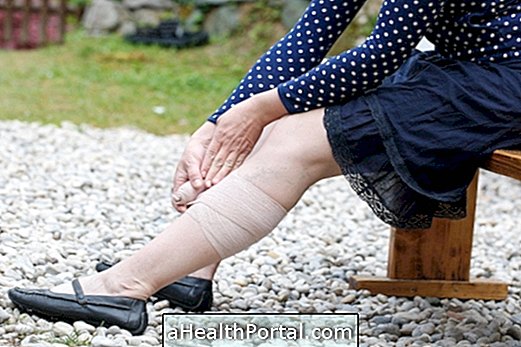
Saline can be used to treat a lack of fluid or salt in the body, which can occur due to episodes of diarrhea, vomiting, gastric aspiration, digestive fistula, excessive sweating, extensive burns or bleeding. Know the symptoms of dehydration.
The administration should be done directly in the vein, by a health professional.
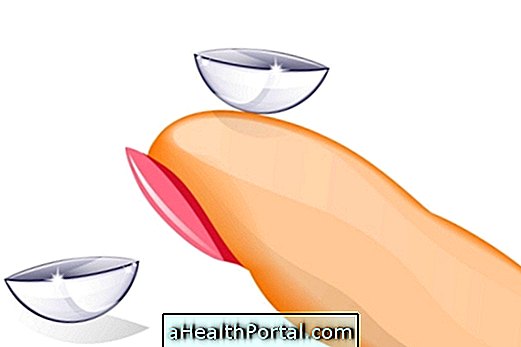
2. Eye cleansing

Saline can also be used for eye cleaning, but a closed, sterile package should always be used. For this, the ideal is to opt for individual packs of single use, which can be found in pharmacies or in the supermarket.
To facilitate cleaning with saline, sterile dressings soaked with this solution can be used.
3. Washing of burns or wounds

The lavage of burns or wounds with saline must always be performed from the center to the periphery and may be performed by a health professional in the hospital or at home, in order to eliminate residues from the region that is susceptible to infections.
Here's how to do a wound dressing at home.
4. Nebulisations

Nebulization with saline solution is a great treatment for sinusitis, colds or flu, as it helps to humidify the airways and to fluidize the secretions, unclogging the airways, thus facilitating breathing. Here's how to do nebulization for sinusitis.
In addition, saline is also widely used to dilute medications such as budesonide, ipratropium bromide or salbutamol, for example, which prolongs the nebulization time.
5. Nose cleaning

A great way to unclog the nose is to do a nasal lavage with saline and a needleless syringe, because through the force of gravity the water enters through one nostril and leaves the other, without causing pain or discomfort, eliminating the secretions.
In addition, it is also a good way to keep the nose properly clean, being useful for anyone who has any respiratory allergy, rhinitis or sinusitis, for example. Here's how to do the nasal wash.
6. Medication vehicle

In certain situations, saline can also be used as a drug carrier, and can then be administered directly into the vein.
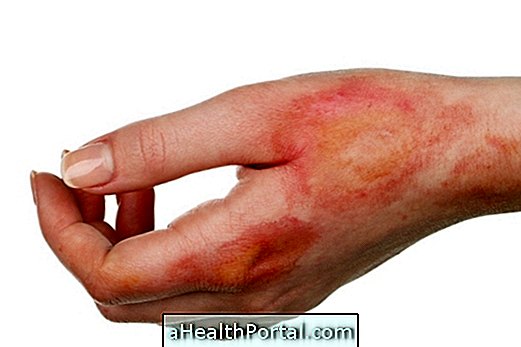
Possible side effects
Saline is generally well tolerated and rarely causes side effects. In addition, adverse reactions depend on the route of administration, and the main side effects include edema, erythema, infection and injection site abscess, thrombophlebitis, electrolyte imbalances, pontic myelinolysis, hyperchloremia and hypernatremia.
Who should not use
Saline should not be used in patients with hypersensitivity to sodium chloride or any other component of the product. In addition, saline should not be used intravenously in patients with hypernatremia, decompensated heart failure, renal insufficiency or generalized swelling.