Allergy is an immune reaction of the body that occurs whenever the individual inhales, ingests or touches an allergen (substance that causes allergy). Children are more likely to develop some kind of allergy than adults, especially food allergies, but in this case, as the digestive system matures the allergy can be naturally eliminated. Children often overcome allergies to milk, eggs and wheat from the age of six, but allergies to peanuts, nuts, fish and seafood, usually last a lifetime.
Symptoms of allergy in children
Allergy symptoms in children may be:
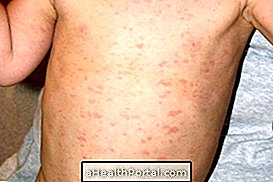
- Reddish and swollen plaques on the body;
- Swollen lips and tongue;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Diarrhea;
- Cramps;
- Gases;
- Itchy nose;
- Frequent sneezing;
- Shortness of breath.
If allergy is suspected, contact your pediatrician.
Diagnosis of allergy in children
The diagnosis of allergy in children can be made through exposure to the allergen and observation of the symptoms that the child presents. Physicians and parents should closely observe any signs of allergy in the child and try to identify what is causing the reaction and then perform tests to detect allergies, which can be through blood tests, skin tests (done through the skin ). They can be done in the tender age, but it is more reliable after 3 years.
For example, if your child always wakes up with very patchy eyes (beyond normal) or if your eyes are always reddish or slightly swollen you should see if your child has any allergies to soap powder, fabric softener or to the fabric of the sheets and blankets, for example.
Treatment for allergy in children
The treatment for allergy in children is to avoid contact with the substance that causes allergy, and if there is any accidental exposure, the doctor may indicate the ingestion of an antihistamine to relieve allergy symptoms. But if your child develops more severe symptoms, such as heavily swollen tongue and difficulty breathing, one should take it to the doctor promptly.