Menstrual bleeding is one that occurs outside of the menstrual cycle, or when there is abundant menstruation for more than 7 days. It can have several causes and is one of the most frequent complaints in gynecological offices.
Excessive menstrual bleeding, scientifically called menorrhagia, can be dangerous because it causes a marked decrease in iron and anemia, reducing the amount of oxygen in the body. Also, depending on the cause of the excessive bleeding, the woman may have a serious health problem, such as a cancer and so it is important to get medical help.

Treatment for menstrual bleeding
Treatment for menstrual bleeding depends on the cause of the excessive bleeding. Thus, in cases related to the production of hormones, usually the remedies to stop menstrual bleeding are oral contraceptives. In case of infection, it is recommended to take the most appropriate antibiotic medicine. In more serious cases, such as uterine fibroid or cancer, hysterectomy surgery may be indicated to remove part or all of the uterus.
See examples of remedies and more treatment options to stop prolonged menstruation.
Symptoms of menstrual bleeding
The characteristic symptom of menstrual bleeding is the loss of blood abundant in the vagina, for more than 7 days. Other symptoms that usually accompany menstrual bleeding are:
- Pain in the intimate region;
- Menstruation with large lumps;
- Abdominal swelling;
- Easy fatigue;
- There may be a fever.
When the woman feels these symptoms she should seek a gynecologist to perform physical, gynecological, blood, ultrasound examination in order to diagnose the cause and start the appropriate treatment.
Causes of menstrual bleeding
The causes of menstrual bleeding can be diverse, being related to hormonal, physical or illness factors that include:
- Modifications of the uterus, such as myoma, polyps, adenomyosis and cancer;
- Changes in blood clotting;
- Hormonal problems, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism or lack of ovulation;
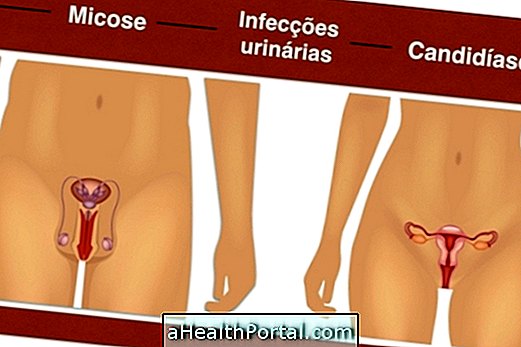
- Infection in the uterus, urinary tract or bladder;
- Use of oral contraceptives;
- Pregnancy or miscarriage;
- Bumps in the abdominal or pelvic region.
When it is not possible to identify the cause of excessive bleeding, it can be considered that the woman suffers from dysfunctional uterine bleeding that has no organic cause and leads to uncontrolled growth of the lining of the uterus, causing bleeding and increasing the chances of developing cancer of the endometrium.