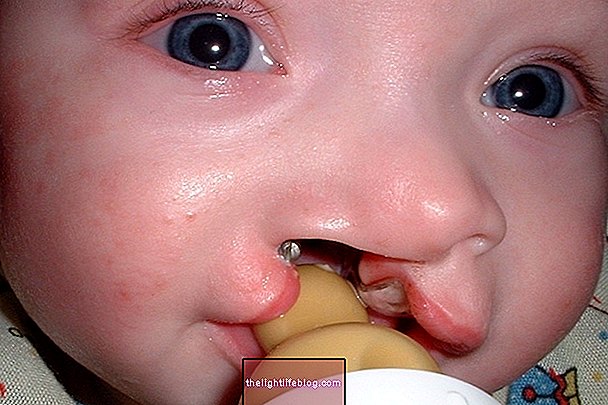
Neurofibromatosis, also known as Von Recklinghausen's disease, is a hereditary disease that manifests itself around the age of 15 and causes abnormal growth of nervous tissue throughout the body, forming small nodules and external tumors, called neurofibromas.
Generally, neurofibromatosis is benign and does not present any health risk, however, as it causes the appearance of small external tumors, it can lead to bodily disfigurement, which makes the affected people intend to have surgery to remove them.
Although neurofibromatosis has no cure, as tumors can grow back, treatment with surgery or radiation therapy can be tried to try to reduce the size of the tumors and improve the aesthetic appearance of the skin.

Neurofibromatosis tumors called neurofibromas
Main types of neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis can be divided into three types:
- Neurofibromatosis type 1: caused by mutations in chromosome 17 that reduce the production of neurofibromine, a protein used by the body to prevent the appearance of tumors. This type of neurofibromatosis can also cause loss of vision and impotence;
- Neurofibromatosis type 2: caused by mutations in chromosome 22, decreasing the production of merlina, another protein that suppresses the growth of tumors in healthy individuals. This type of neurofibromatosis can cause hearing loss;
- Schwannomatosis: it is the rarest type of the disease in which tumors develop in the skull, spinal cord or peripheral nerves. Generally, symptoms of this type appear between the ages of 20 and 25.
Depending on the type of neurofibromatosis, symptoms may vary. So, check out the most common symptoms for each type of neurofibromatosis.
What causes neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is caused by genetic changes in some genes, especially chromosome 17 and chromosome 22. In addition, rare cases of Schwannomatosis appear to be caused by changes in more specific genes such as SMARCB1 and LZTR. All altered genes are important in inhibiting the production of tumors and, therefore, when they are affected, they lead to the appearance of tumors characteristic of neurofibromatosis.
Although most diagnosed cases are passed from parents to children, there are also people who may never have had any cases of the disease in the family.
How the treatment is done
Treatment for neurofibromatosis can be done through surgery to remove tumors that are putting pressure on organs or through radiation therapy to reduce their size. However, there is no treatment that guarantees a cure or that prevents the appearance of new tumors.
In the most severe cases, in which the patient develops cancer, it may be necessary to undergo treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy directed at malignant tumors. Find out more details of the Treatment for neurofibromatosis.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
.jpg)