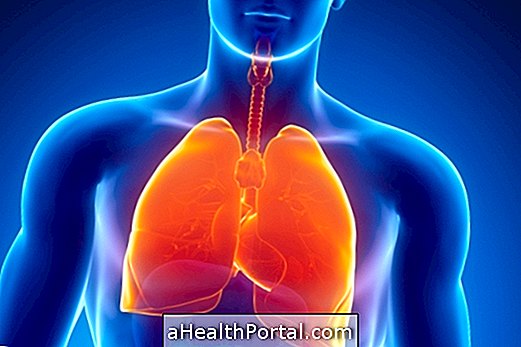
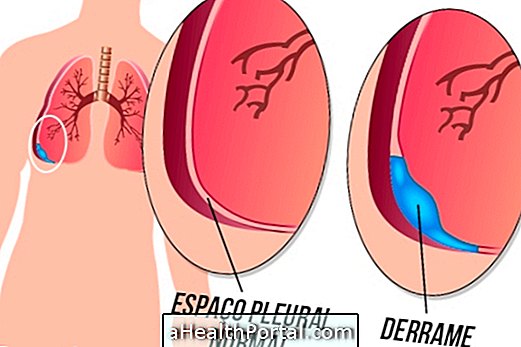
Pleural effusion occurs due to the excessive accumulation of fluid in the pleural space, which is the space created between the lung and the outer membrane that covers it.
This buildup hampers normal lung work and therefore breathing can be severely affected, and treatment should be done as soon as possible in the hospital to remove excess fluid.
How is pleural effusion
In normal situations, the amount of fluid in the pleural space is very small, about 10 mL, and results in a perfect balance between its production and absorption. However, when there is a health problem such as lung infections or heart failure, this balance can be affected leading to excessive fluid accumulation.
Since the fluid can not be absorbed properly it will slowly accumulate, increasing pressure on the lung, which makes breathing difficult, leading to symptoms such as chest pain and a feeling of shortness of breath, for example.
What May Cause Stroke
The main causes of pleural effusion are related to inflammation of lung or pleural tissues, and include:
- Pneumonia;
- Tuberculosis;
- Lung cancer;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Lupus.
However, the stroke can also be caused by problems that lead to increased fluid throughout the body such as decompensated heart failure, cirrhosis or advanced kidney disease.
How to confirm the stroke

The best way to confirm the presence of a pleural effusion is to have an x-ray of the chest to see if there is accumulation of fluid, which is represented by a white area in the lung.
In most cases, the cause of pleural effusion is already known, as in cases of heart failure, however, when the stroke appears without an apparent cause, further tests may be necessary to identify the cause and initiate appropriate treatment.
How is the treatment done?
The pleural effusion is treated when it is very large and causes symptoms such as severe pain or shortness of breath, because when it is small it can be absorbed by the body, being only necessary to make new x-ray to observe its evolution.
In the chaos in which treatment is needed, the doctor uses a needle and syringe to traverse the chest wall and reach into the fluid-filled space, removing the excess.
Since there is a great risk that the pleural effusion returns a few weeks after being aspirated it is very important to identify what is causing the problem by initiating appropriate treatment of the cause.
Physiotherapy for pleural effusion
After removal of excess fluid, the doctor may recommend that respiratory physiotherapy consisting of a set of breathing exercises taught by the physiotherapist that help the lung return to its normal size after being pressed by the stroke.
These exercises are important for reducing discomfort in breathing, but also for increasing the amount of oxygen in the body.
Main symptoms
Early symptoms that may indicate the development of a pleural effusion include:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Feeling of shortness of breath;
- Chest pain, which worsens upon deep breath;
- Fever above 37.5 ° C;
- Persistent cough.
In most cases, these symptoms do not appear in small pleural effusions, and even when they appear they can be associated with their causes, such as heart failure or pneumonia. Therefore, it is always recommended to have an x-ray to evaluate the possibility of a stroke, especially in decompensated cases or when the symptoms are very intense.