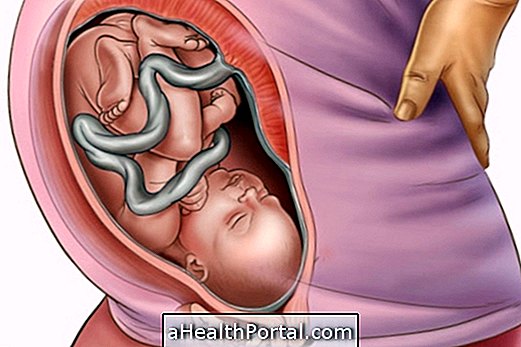
The premature baby is one who is born before 37 weeks gestation, since the ideal is that birth occurs between 38 and 41 weeks. The premature babies with the highest risk are those born before 28 weeks or who have a birth weight of less than 1000g.
Premature infants are small, have low weight, breathe and feed themselves with difficulty and are more likely to have health complications, needing to stay in the hospital until their organs work well, avoiding complications at home and favoring their growth.

Growth of premature infants up to 2 years
After discharge and proper care of food and health at home, the baby should grow normally following his own standard. It is common for it to be a little smaller and leaner than other children of the same age, as it follows a growth curve suitable for premature infants.
Up to 2 years of age, the baby's adjusted age must be used to evaluate its development, making the difference between 40 weeks (normal age to be born) and the number of weeks at the time of delivery.
For example, if premature was born at 30 weeks' gestation, you need to make a difference of 40-30 = 10 weeks, which means that the baby is actually 10 weeks younger than other babies your age. Knowing this difference, it is possible to understand why premature infants seem smaller in relation to other children.
Growth of premature infants after 2 years
After 2 years, the premature baby will be evaluated in the same way as the children who were born at the right time, and it is no longer necessary to calculate the adjusted age.
However, it is common for premature infants to remain slightly smaller than other infants of the same age, as it is important that infants continue to grow in height and gain weight, which represents adequate growth.
How long does the baby stay in the hospital?
The baby will have to be hospitalized until he learns to breathe and suckles himself, gains weight until he reaches at least 2 kg and until his organs function normally.
The more premature, the greater the difficulties and longer the time of hospitalization of the baby, being normal that he stays a few months hospitalized. During this period, it is important that the mother withdraws milk to feed the child and that the family informs about the health condition of the baby. Learn more about what to do while the baby is in the hospital.

Possible health complications
The possible health complications of prematurity are respiratory difficulties, heart problems, cerebral palsy, vision problems, deafness, anemia, reflux and infections in the gut.
Premature infants are more likely to have health complications and difficulty feeding because their organs have not had enough time to develop properly. See what the feeding of the premature baby should look like.