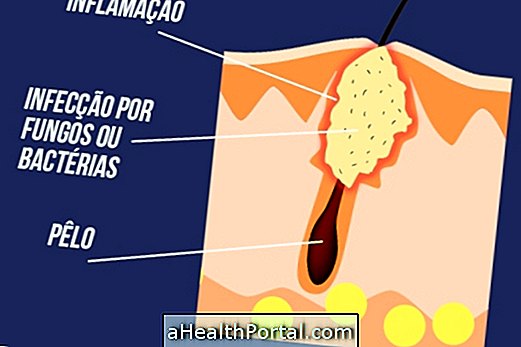
Inflammation happens when the body fights an infection or injury, and it is a natural process that is part of the body's immune system. Generally, inflammation causes heat, redness, swelling and pain and can be caused by infections by bacteria, viruses or parasites in the body or by other factors such as poison, heat, radiation exposure or trauma, such as when you have a sprain or break a bone.
Inflammation can happen in several parts of the body such as the ear, intestine, gum, throat or uterus for example and this can be acute or chronic depending on how long your symptoms take to appear or what the inflammation leads to being cured.
Possible Symptoms of Inflammation
The main symptoms that indicate inflammation are:
- Swelling or edema;
- Pain when touching;
- Redness or blushing;
- Feeling of heat.
These are the main 4 signs that usually indicate the presence of an inflammatory process and in the presence of some of these symptoms should consult the doctor as soon as possible so that this can start the treatment.
In addition, depending on the site of the inflammation, other signs and symptoms such as swollen glands and white spots may develop in the case of inflammation of the throat or pain, fever and the discharge of thick yellowish liquid in case of ear infection.
How to cure inflammation
To cure inflammation must be made a treatment anti-inflammatory medicines that can be of 2 types:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories : such as ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid, or naproxen, which are generally used to treat more simple inflammations such as throat inflammation or earache, for example;
- Anti-inflammatories Corticosteroids : such as Prednisolone or Prednisone, which are generally used only in cases of more severe or chronic inflammation such as psoriasis or some chronic candidiasis.
The action of anti-inflammatories will help reduce discomfort and the effects of inflammation in the body, reducing the pain, swelling and redness felt.
Why Inflammation Happens
Inflammation occurs when substances in the body are released, such as histamine, which give rise to the inflammatory response in the body. These substances are released when the body fights an infection or injury and increases blood supply at the site of the injury.
In addition, there is the production of inflammatory substances that increase the permeability of blood vessels at the site and there is a process called chemotaxis, a chemical process where blood cells such as neutrophils and macrophages are attracted to the site of the lesion to fight the causative agents inflammation and control bleeding.
What is the difference between acute and chronic inflammation
The difference between acute and chronic inflammation is the intensity of the symptoms felt and the time it takes to emerge as well as the time that the inflammation leads to being cured. While in acute inflammation are present the typical signs of inflammation, such as heat, redness, swelling and pain and this persists for a short time, in chronic inflammation the symptoms senses are not very specific are not visible and this lasts generally more than 3 months .
Tonsillitis and otitis are some examples of acute inflammation, and rheumatoid arthritis, asthma and tuberculosis, examples of chronic inflammation.