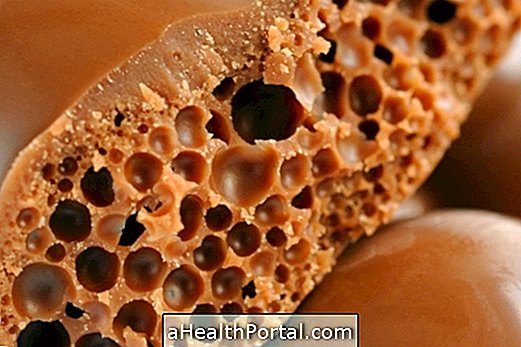
Tripophobia is characterized by a psychological disorder, in which the person has an irrational fear of images or objects that have holes or irregular patterns, such as honeycombs, grouping of holes in the skin, wood, plants or sponges, for example.
People who suffer from this fear feel ill and symptoms such as itching, trembling, tingling and disgust come into contact with these patterns. In more severe cases, tripophobia can lead to nausea, increased heart rate and even panic attacks.
Treatment may include gradual exposure therapy, use of anxiolytics and antidepressants, or psychotherapy.
Possible causes
According to research, people with tripophobia unconsciously associate holes or objects with irregular patterns, usually related to patterns created by nature, to possible situations of danger. This sense of danger is triggered mainly by the similarity between the appearance of the holes with the skin of venomous animals, such as snakes, for example, or with worms that cause diseases in the skin, such as passionate heel. Learn more about the passion fruit heel.
Generally, people who suffer from this phobia can not distinguish situations in which there is or is not danger, being an unconscious reflex that results in reactions that can not be controlled.
Main symptoms
The symptoms that appear in people with tripophobia when exposed to patterns such as lotus seeds, honeycombs, bubbles, strawberries or crustaceans for example, are:
- Nipple;
- Tremors;
- Suores;
- Disgusted;
- Cry;
- Goosebumps;
- Discomfort;
- Increased heart rate;
- Generalized itching and tingling.
In more severe cases, the person may also suffer from panic attacks due to an extreme level of anxiety. Know what to do during a panic attack.

How is the treatment done?
There are several ways to treat this psychological disorder, with exposure therapy being the most effective. This type of therapy helps the person to control the fear by changing their response to the object that causes it and must be done very carefully so as not to cause trauma.
This therapy should be done with the help of a psychologist through exposure to the stimulus that causes the phobia gradually. Through dialogue, the therapist uses techniques of relaxation, so that the person faces the fear, until the discomfort diminishes.
This therapy can be combined with other techniques that help reduce anxiety and treat this fear:
- Taking medicines to help reduce anxiety and panic symptoms such as beta blockers and sedatives;
- Practice relaxation techniques like yoga for example;
- Exercise to reduce anxiety - see some tips to control anxiety.
Tripophobia is not yet recognized in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders of the American Psychiatric Association, but some studies prove that the phobia exists and causes symptoms that condition people's lives.