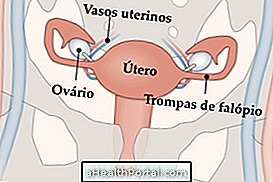
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation, which can be primary, when menstruation does not reach teenage girls between the ages of 14 and 16, or secondary, when menstruation stops coming in women who have menstruated before.
Amenorrhea can occur from a number of causes, some of which are natural, such as pregnancy, breastfeeding or contraceptive use on an ongoing basis, or from certain diseases, from defects in the woman's reproductive system, changes in ovarian hormones and even from stress, or excessive exercise.

Types of amenorrhea
The absence of menstruation can happen due to several causes, being classified in 2 types:
- Primary amenorrhea : is when menstruation of girls from 14 to 16 years does not appear, as would be expected by the period of development of the body. In these cases, the gynecologist will perform the clinical examination and request blood tests and ultrasound to investigate if there are anatomical changes of the reproductive system or alterations of hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, TSH, FSH and LH.
- Secondary amenorrhea : occurs when menstruation stops coming for some reason, in women who menstruate previously, for 3 months, when menstruation was regular or for 6 months, when menstruation was irregular. The research is also done by the gynecologist, with clinical gynecological examination, dosages of hormones, as well as transvaginal or pelvic ultrasound.
It is important to take the test for pregnancy whenever there is amenorrhea, it is possible to become pregnant even in cases of irregular menstrual cycle or that was missing for a long time.
Main causes
The main causes of amenorrhea are pregnancy, breastfeeding and menopause, which are natural causes of the body, in periods in which changes in the levels of the hormones progesterone and estrogen are common.
However, other causes of amenorrhea are caused by diseases, medications or habits, such as:
| Causes | Examples |
| Hormonal imbalance | - Changes in hormones, such as prolactin excess, testosterone, hyper or hypothyroidism; - Brain changes, such as dysregulation or pituitary tumor; - Polycystic ovarian syndrome; - Early menopause. |
Reproductive system disorders | - Absence of uterus or ovaries; - Changes in vaginal structure; - Imperforate hymen, when menstruation has nowhere to go; - Uterine scars or Ashermann's syndrome; |
| Ovulation inhibited by habits of life | - Eating disorders, such as anorexia; - Excess of physical activity, common in athletes; - Very fast weight loss; - Obesity; - Depression, anxiety. |
| Medicines | - contraceptives for continuous use; - Antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, fluoxetine; - Anticonvulsants, such as phenytoin; - Antipsychotic, such as haldol, risperidone; - Antihistamines, such as ranitidine, cimetidine; - Chemotherapy. |
How to treat
The treatment for amenorrhea depends on the cause and is done with the guidance of the gynecologist, who will determine the best option for each case. So, some options are:
- Correction of hormone levels in the body : includes the use of medications to control prolactin and testosterone levels, for example, or replacement of estrogen and progesterone levels to maintain regulated hormone levels.
- Changing lifestyle habits : how to lose weight, have a balanced and healthy diet, moderate physical activity, and treatment of depression and anxiety, if any, according to the psychiatrist's advice.
- Surgery : can restore menstruation and increase the possibility of getting pregnant, as in imperforate hymen, uterine scars and some vaginal changes. However, when there is absence of the uterus and ovary, it is not possible to establish ovulation or menstruation.
Natural treatments can help in some cases of delayed menstruation by altering the menstrual cycle in women without significant deregulation of hormones or other diseases, and some examples are cinnamon tea and agonized tea. See more about what to do and delayed menstruation teas recipes.
It is possible to conceive with amenorrhea
The possibility of pregnancy, in cases of amenorrhea, depends on the cause. Correction of hormones for the normal functioning of the ovary can regulate ovulation and fertility, or they can be induced with the use of medications, such as Clomiphene, for example, which allows pregnancy naturally.
In cases of absence of the ovary it is possible, also, to have a pregnancy, by the donation of eggs. However, in cases of absence of uterus, or important deformities of the reproductive system, which are not resolved with surgery, pregnancy, in principle, is not possible.
It is important to remember that women who have irregular menstruation can get pregnant, although it is more difficult, and therefore, precautions should be taken to avoid an unwanted pregnancy. A discussion with the gynecologist should be held to evaluate the possibilities and treatments for each woman, according to their needs and wishes, regarding pregnancy and contraceptive methods.