Regardless of the cause of vomiting in the child, when she has a sudden vomiting episode with no other associated symptoms such as fever, for example, it is usually not a reason to rush to the emergency room, as vomiting may only be a consequence of transient situations, or by consumption of spoiled or contaminated food, due to sudden movements after eating or a mild virus, for example.
However, there is a greater concern when vomiting is persistent, occurs after the accidental ingestion of medications or when there are other associated symptoms such as fever and malaise, and in these cases, it is necessary to consult as a pediatrician. Understand the main causes of baby fever and how to lower it.
Thus, when the child vomits it is necessary to have some care at home to facilitate its recovery and prevent it from becoming dehydrated, such as:
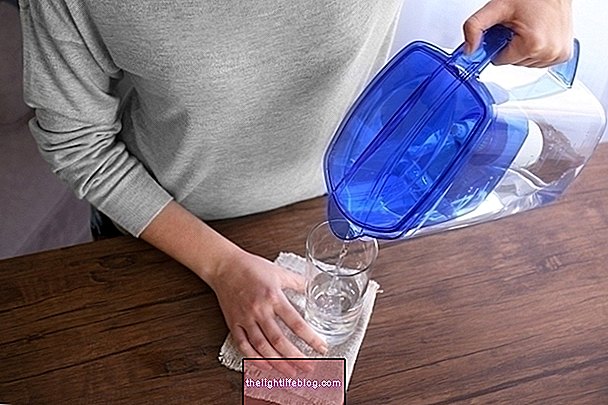
1. Position

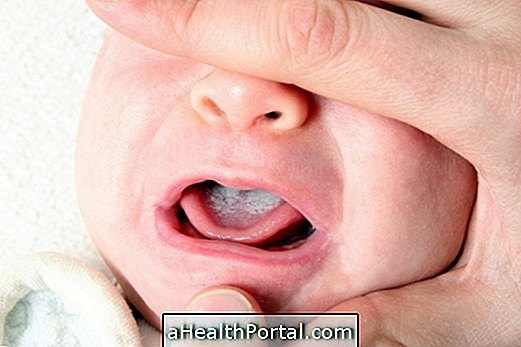
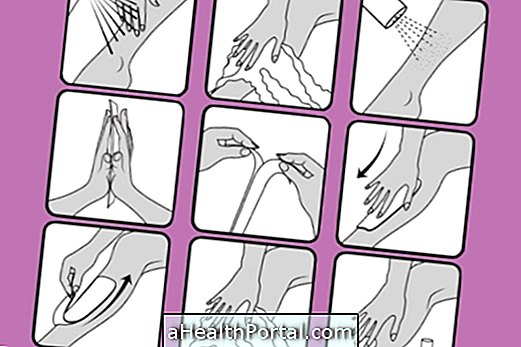
Sit the child, tilt the trunk and hold the forehead until they stop vomiting, as shown in the first image, to facilitate expulsion of vomiting and prevent the child from gasping. If the child is lying down, the child should be turned to the side until he or she stops vomiting to avoid choking on her own vomit.
2. Rehydrate

After the child vomits it is necessary to give him rehydration solutions purchased at the pharmacy or make homemade whey. Learn step by step to prepare homemade whey.
3. Feed

After 2 to 3 hours after the child vomits, she can eat light and easily digestible foods, such as soup, juices, porridges or soup, for example. These foods should be consumed in small amounts to facilitate digestion.
However, fatty foods like red meats and dairy products should be avoided as they are more difficult to digest. Learn more about what should be feeding the child with vomiting and diarrhea.
What to do when your baby vomits
When the baby vomits, it is important not to insist on breastfeeding and, at the next meal, one should breastfeed or bottle as normally. Also, when laying the baby, it should be on the side and not on the back, to avoid suffocation, if you vomit.
However, it is important not to confuse gaggle with vomit, because in the gulp there is a return of the milk without effort and soon after the feeding, in the vomit the return of the milk is sudden, in jet and causes suffering in the baby.
When to take the child to the
It is necessary to consult the pediatrician or go to the emergency room when, in addition to vomiting, the child or baby has:
- High fever, above 38ºC;
- Frequent diarrhea;
- Not being able to drink or eat anything during the day;
- Signs of dehydration such as cracked lips or a small amount of urine with color and strong odor. See the signs of dehydration in children.
In addition, even if the child or baby vomits without fever, if the vomiting persists for more than 8 hours, and the child does not tolerate liquid foods, it is also recommended to consult the pediatrician or go to the emergency room. It is also important to go to the hospital when the fever does not go away even with medicines.