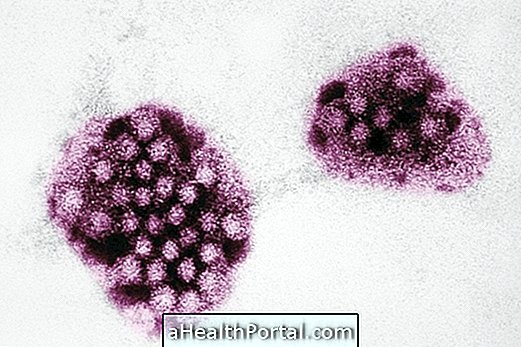
The duration of measles is approximately 8 to 14 days, but in most individuals it lasts 10 days . Four days before the first symptoms of the disease appear until their complete remission, the individual can contaminate others and so it is very important that everyone take the triple-virus vaccine that protects against measles, mumps and rubella.
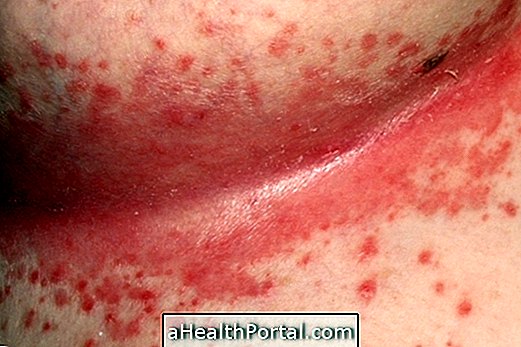
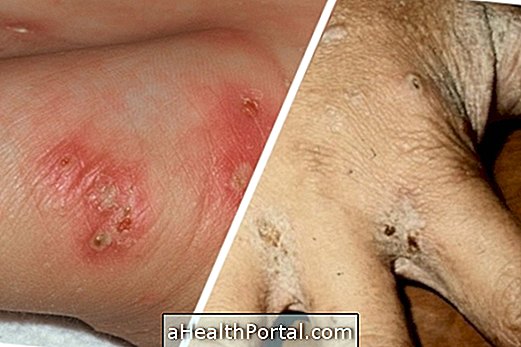
Usually from the 4th day of the virus's incubation period the bluish-white spots appear inside the mouth and the blotchy spots on the skin, initially close to the scalp and progressing from the face to the feet. The spots from inside the mouth tend to disappear after 2 days of the appearance of the spots on the skin and these remain for approximately 6 days.
Possible Complications
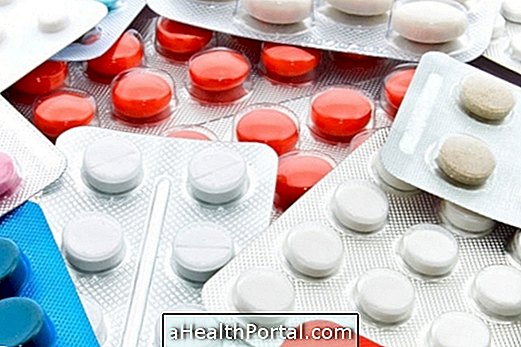
During the measles period it is recommended to control fever and malaise with antipyretic and analgesic medicines. But acetylsalicylic acid medicines like AAS, Aspirin, Doril and Mejoral should not be taken, for example, because they increase the risk of bleeding. In case of measles it is recommended to take a medicine based on Paracetamol.
Measles is a self-limiting disease that usually does not lead to complications, but the disease can evolve causing:
- Bacterial infections such as pneumonia or otitis media;
- Ecchymosis or spontaneous bleeding, since the amount of platelets can decrease greatly;
- Encephalitis, a type of brain infection;
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, a serious complication of measles that produces brain damage.
These complications of measles are more common in malnourished individuals or those with compromised immune systems.
Prevention
The most effective way to prevent measles is through vaccination. The measles vaccine should be taken in two doses, the first in childhood between 12 and 15 months and the second between 4 and 6 years of age. When vaccinated the individual is protected and can not contract the disease.
Adolescents and adults who have not been vaccinated in childhood may take a single dose of the vaccine and be equally protected.