Flies can transmit diseases because they are in constant contact with decaying materials, such as feces or dirt, carrying bacteria capable of causing some diseases, such as ringworm, berne, pinworm, trachoma and dysentery, for example.
These diseases can be transmitted by domestic flies because the bacteria usually stick to their fur and can be released on the food or inside wounds on the skin when they come in direct contact with humans.
In addition, flies may ingest bacteria that remain alive for a few days inside the animal, being deposited in human food when the fly uses saliva to feed.
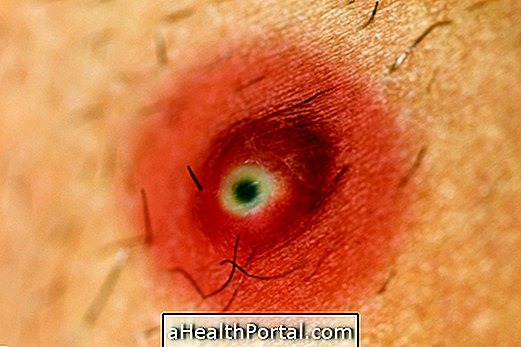
But another disease caused by flies is human myiasis, which may be berne or pinworm, which occur after the deposition of eggs that become larvae, which feed on the tissues, from a wound, for example.

Care to avoid house flies
Some simple precautions to avoid domestic flies and, consequently, the diseases they transmit are:
- Do not let garbage accumulate more than 2 days indoors;
- Wash the bottom of the container where the waste is placed with bleach or chlorine once a week;
- Use a dish or other utensil to cover the food, avoiding exposing it;
- Avoid eating food that was in direct contact with flies;
- Laying nets against flies and mosquitoes on windows;
- Use a mosquito net for sleeping, especially for babies.
However, if flies can develop indoors even following these tips, there are ways to eliminate them, such as using insecticides, traps, or vaporizers.