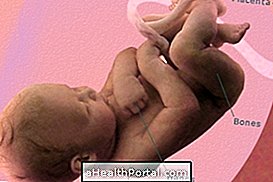
Normal delivery is best for the mother and the baby because in addition to the recovery being faster, allowing the mother to take care of the baby soon and without pain, the mother's risk of infection is lower because there is less bleeding and the baby also has less risk of respiratory problems.
However, a cesarean section may be the best birth option in some cases. Pelvic presentation (when the baby is seated), twins (when the first fetus is in an anomalous position), when there is cephalopelvic disproportion or in cases where there is suspicion of detachment of the entire placenta or placenta occluding the birth canal.
Differences between normal and cesarean delivery
Normal labor and cesarean sections vary between labor and the postpartum period. Therefore, see the following table the main differences between normal and cesarean delivery.
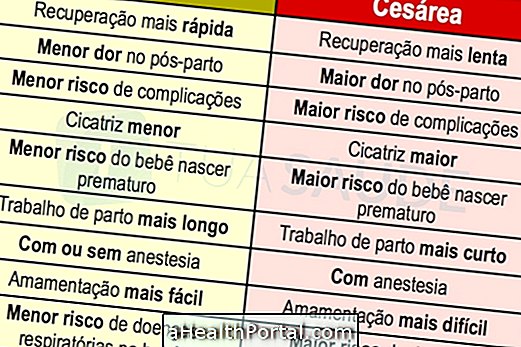
In cases of normal birth, the mother can usually get up soon to take care of the baby, she does not have pain after the birth and the future deliveries are easier, they last less time and the pain is still smaller, whereas in the cesarean, the woman can only lifting between 6 and 12 hours after giving birth, has pain and future deliveries of cesarean section are more complicated.
The woman may not feel pain during normal delivery if she receives epidural anesthesia, which is a type of anesthesia that is given in the back so that the woman does not feel pain during labor and does not harm the baby. Learn more at: Epidural Anesthesia.
In cases of normal delivery, where the woman does not want to receive anesthesia, it has the natural birth name, and the woman can adopt some strategies to relieve pain such as changing position or controlling breathing. Read more in: How to relieve pain during labor.
Indications of the cesária
The cesarean section is indicated in the following cases:
- Pregnancy of twins when the first fetus is pelvic or in some anomalous presentation;
- Acute fetal distress;
- Very large babies, over 4, 500 g;
- Baby in transverse or sitting position;
- Placenta previa, placental abruption or abnormal position of the umbilical cord;
- Congenital malformations;
- Maternal problems such as AIDS, genital herpes, severe cardiovascular or pulmonary disease or inflammatory bowel disease;
- Performing two previous cesarean sections.
In addition, cesarean section is also indicated when attempting to induce labor through medication (if a labor test is attempted) and it does not evolve. However, it is important to remember that cesarean delivery causes increased risks of complications during and after surgery.
What is humanized childbirth?
Humanized delivery is a delivery in which the pregnant woman has control and decision on all aspects of labor such as position, place of birth, anesthesia or presence of family members, and where the obstetrician and the staff are present to put the decisions into practice and wishes of the pregnant woman, taking into account the safety and health of the mother and baby.
Thus, in humanized labor, the pregnant woman decides whether she wants a normal or caesarean delivery, anesthesia, bed or water, for example, it is up to the medical team to respect these decisions, as long as they do not endanger the mother and the baby. To know more advantages of humanized childbirth see: How is a humanized childbirth?
Find out more about each type of delivery in:
- Advantages of normal birth
- How is a cesária
- Phases of Labor