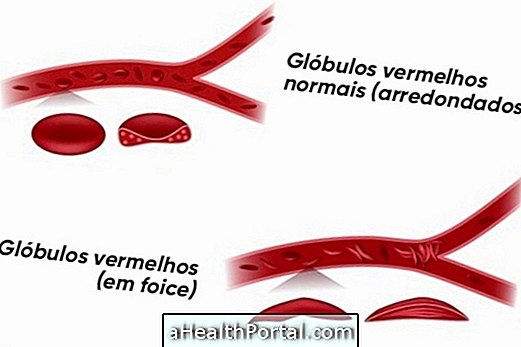
Thrombosis in pregnancy arises when a blood clot forms that blocks a vein or artery, preventing blood from passing through the site.
Although thrombosis may occur in anyone, this complication is most common during gestation, as the ability to coagulate and blood flow is altered by the hormonal changes that occur and the compression of the uterus on the blood vessels.
Most Common Types of Thrombosis
The pregnant woman has a 5 to 20 times greater risk of developing thrombosis than someone else, and the most common types include:
- Deep venous thrombosis : it is the most common type of thrombosis, and it affects the legs more frequently, although it can appear in any region of the body;
- Hemorrhoidal thrombosis : may occur in hemorrhoids caused by the baby's weight or during delivery;
- Placental thrombosis : caused by a clot in the placenta veins, which may lead to miscarriage in more severe cases. Learn more about this situation in placental thrombosis.
- Umbilical Cord Thrombosis : Although rare, this type of thrombosis occurs in the umbilical cord vessels, preventing blood flow to the baby. Know when and how to treat umbilical cord thrombosis;
- Cerebral thrombosis in pregnancy : caused by a clot in the brain, very serious situation and causes symptoms of stroke.
Pregnancy thrombosis, although rare, is more common in women over 35 years of age who have had an episode of thrombosis in an earlier pregnancy, are pregnant with twins, or are overweight. This condition is dangerous, and when identified, should be treated by the obstetrician with anticoagulant injections, such as heparin, during gestation and 6 weeks postpartum.
What are the symptoms
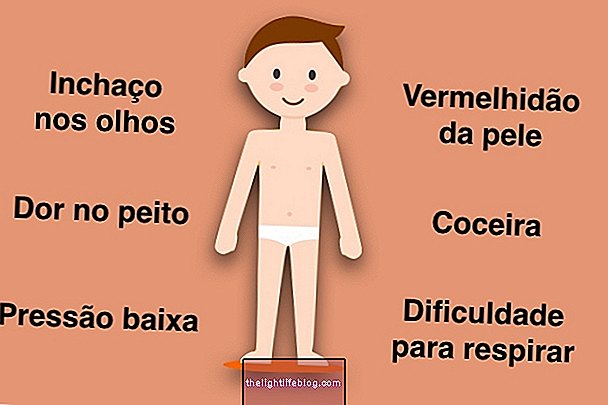
The symptoms of thrombosis in pregnancy arise especially in the legs and include:
- Pain in the leg, which worsens when walking or bending the foot upwards;
- Redness and swelling of the leg;
- Hot skin;
- Increased local veins.
During pregnancy, these symptoms do not always confirm the thrombosis, because they may occur due to a greater tendency to retain fluid in the legs, so the pregnant woman should consult the obstetrician to make an ultrasound and miss the diagnosis of thrombosis.
In the presence of any of these symptoms, the pregnant woman should immediately call 192 or go to the emergency room, as thrombosis is a serious disease, which can cause pulmonary embolism in the mother when the clot travels to the lungs, generating symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing up blood, or chest pain.
When the thrombosis occurs in the placenta or the umbilical cord, there are usually no symptoms, but the decrease in baby's movements may indicate that something is wrong with the blood circulation, and it is also important to seek medical attention in this situation.
How to confirm the diagnosis
After the clinical evaluation of the physician, confirmation of the diagnosis of thrombosis is done by the Doppler ultrasound examination, which can identify the blood flow and the presence of clots.

How is the treatment done?
Thrombosis in pregnancy has a cure, and treatment should be indicated by the obstetrician and usually includes the use of heparin injections, which help dissolve the clot, decreasing the risk of new clots.
In most cases, the treatment for thrombosis in pregnancy should be maintained until the end of gestation and 6 weeks after delivery, because during the birth of the baby, either through normal delivery or cesarean section, the abdominal and pelvic veins of women suffer lesions which may increase the risk of clot formation.
How to prevent thrombosis in pregnancy
Some precautions to avoid thrombosis in pregnancy are:
- Use compression stockings from the beginning of pregnancy, to facilitate blood circulation;
- Do regular light exercise, such as walking or swimming, to improve blood circulation;
- Avoid staying more than 8 hours lying down or more than 1 hour sitting;
- Do not cross your legs, as it hinders the circulation of blood in the legs;
- Have a healthy diet, low in fat and high in fiber and water;
- Avoid smoking or socializing with people who smoke, because cigarette smoke can increase the risk of thrombosis.
This care should be done mainly by the pregnant woman who had thrombosis in the previous pregnancy. In addition, the pregnant woman must inform the obstetrician who has had thrombosis to start treatment with heparin injections, if necessary, in order to prevent the onset of a new thrombosis.