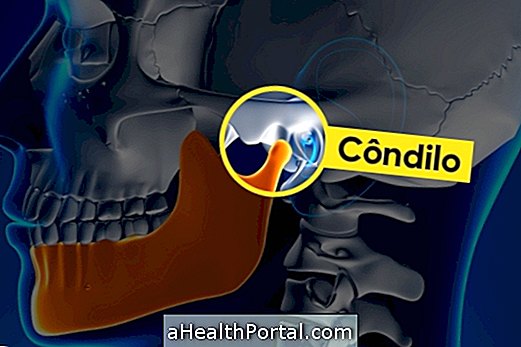
Gingival recession, also known as a receding gingiva or receding gingiva, occurs when there is a decrease in the amount of gum that covers the tooth, leaving it more exposed and apparently longer. It can happen only in one tooth or in several teeth at the same time.
This problem arises slowly but worsens over time, and if left untreated when the first signs appear, it can have serious consequences, which can lead to infection or even lead to tooth loss and damage to bone and tissue. jaw.

How is the treatment done?
Gingival retraction is healing, or it can be controlled if it is well treated when the first symptoms appear. Eating a balanced diet, quitting smoking or removing piercings that may be at the root of the problem are easy steps that can solve it. In addition, it is important to brush your teeth more correctly, less aggressively, with a soft brush, at least twice a day, along with flossing every day. Here's how to brush your teeth properly.
Even so, as soon as the first signs and symptoms appear, one should consult a dentist who can advise the best treatment, depending on the cause and severity of gingival retraction:
- Infection : The dentist in addition to treating the problem, may also prescribe a mouthwash, gel or an antiseptic paste;
- Accumulation of tartar : a dental cleaning should be done at the dentist;
- Periodontitis : Scaling and root planing should be done;
- Poorly positioned teeth : should be corrected with the use of dental appliance in order to align them;
- Use of medicines that cause dry mouth : review with your doctor if there is another remedy with fewer side effects or use a product to reduce dryness of the mouth.
Normally, due to exposure of the tooth root, tooth sensitivity may occur and this problem should also be addressed. Usually, use of mouthwash and specific toothpastes can reduce tooth sensitivity. If these measures are not enough, fluoride can be used, or resin treatment may be used, which consists in restoring the tooth with acrylic resin in order to cover sensitive exposed areas. Learn more about treating tooth sensitivity.
When to have gingival surgery
In more severe cases, the dentist may suggest a gingival surgery consisting of covering the exposed portion of the root of the tooth, repositioning the gum or using a tissue graft usually made from gum removed from the roof of the mouth.
The success of the surgery depends on the severity of the problem, as well as the person's age, healing capacity, gum thickness, and other factors such as cigarette smoking and oral hygiene habits.
Home treatment for gingival retraction
Since gingival retraction is caused by various causes that strike the gums, it can be attenuated or prevented with the following home remedies:
1. Myrrh oral elixir
The antimicrobial and astringent properties of myrrh help to kill bacteria and protect the gingival tissue and can therefore help prevent the appearance of retracted gingiva.
Ingredients
- 125 ml of warm water;
- 1/4 teaspoon of sea salt;
- 1/4 teaspoon of myrrh extract.
Method of preparation
Mix the ingredients and after cleaning the teeth use 60 ml to rinse carefully.
2. Oral Elixir of salva
Daily mouthwashes with a solution of sea salt and salt tea help prevent gum disease. Both are antiseptic, relieve inflammation and promote healing. Being astringent also helps to tone the gingival tissue.
Ingredients
- 250 ml of boiling water;
- 2 teaspoons of dried sage;
- 1/2 teaspoons of sea salt.
Method of preparation
Turn the water over the saver, cap and let stand for 15 minutes. Strain and combine the sea salt and let to blend. Use about 60 ml and rinse well after cleansing the teeth. Use within 2 days.
3. Hydras paste
This paste of hydraste and myrrh exerts an intense curative action on the inflamed gums, being a good option if the retracted gums are also red and inflamed.
Ingredients
- Myrrh extract;
- Powder of hydraste;
- Sterile gauze.
Method of preparation
Mix a few drops of myrrh extract to the hydraste powder to make a thick paste. Wrap in sterile gauze and place on affected area for one hour. Repeat twice a day.

What are the possible causes
Gingival retraction can occur at any age and in healthy mouths, and can be caused by different factors, such as:
- Gum infection;
- Poor dental positioning;
- Accumulation of tartar in the teeth;
- Inheritance, there being no apparent cause;
- Injuries caused by brushing your teeth very hard or with very hard brushes;
- Periodontal disease, which may occur due to insufficient oral hygiene;
- Hormonal changes in women;
- Use of piercings in the mouth that can cause lesions on the gums;
- Weakening of the immune system due to leukemia, AIDS or treatments such as chemotherapy, for example;
- Use of medicines that make the mouth drier;
- Dental procedures, such as prosthesis application, tooth whitening or dental appliance application;
- Bruxism, which is a grinding or a strong tightening of the teeth, leading to its wear and the destruction of the gum tissue.
In addition, gingival recession is more common with advancing age or in people smokers, with diabetes or who make a poor diet.
It is important to go to the dentist regularly in order to detect the first signs of gingival retraction in order to prevent its evolution.
Symptoms of gingival retraction
In addition to a gum shrinkage that exposes the tooth further and makes the base more yellowish, symptoms of gingival retraction may also include bleeding gums after brushing or flossing, increased tooth sensitivity, redder gums, bad breath, pain in the teeth and gums and, in more severe cases, loss of teeth.